Working with relational data
Lecture 5
Dr. Benjamin Soltoff
Cornell University
INFO 5001 - Fall 2025
September 9, 2025
Announcements
Announcements
- Homework 1 due Wednesday at 11:59pm
- Office hours schedule
fill vs. color
- Use
fillwhen a geom is filled - Use
colorwhen a geom is outlined
Learning objectives
- Introduce relational data
- Demonstrate how tables can be linked to one another
- Demonstrate methods in {dplyr} for linking and merging related tables
- Practice joining tables
Relational joins
Introduction to relational data
- Multiple tables of data that when combined together accomplish goals
- Relations define the important element, not just the individual tables
- Relations are defined between a pair of tables
- Relational verbs
- Mutating joins
- Filtering joins

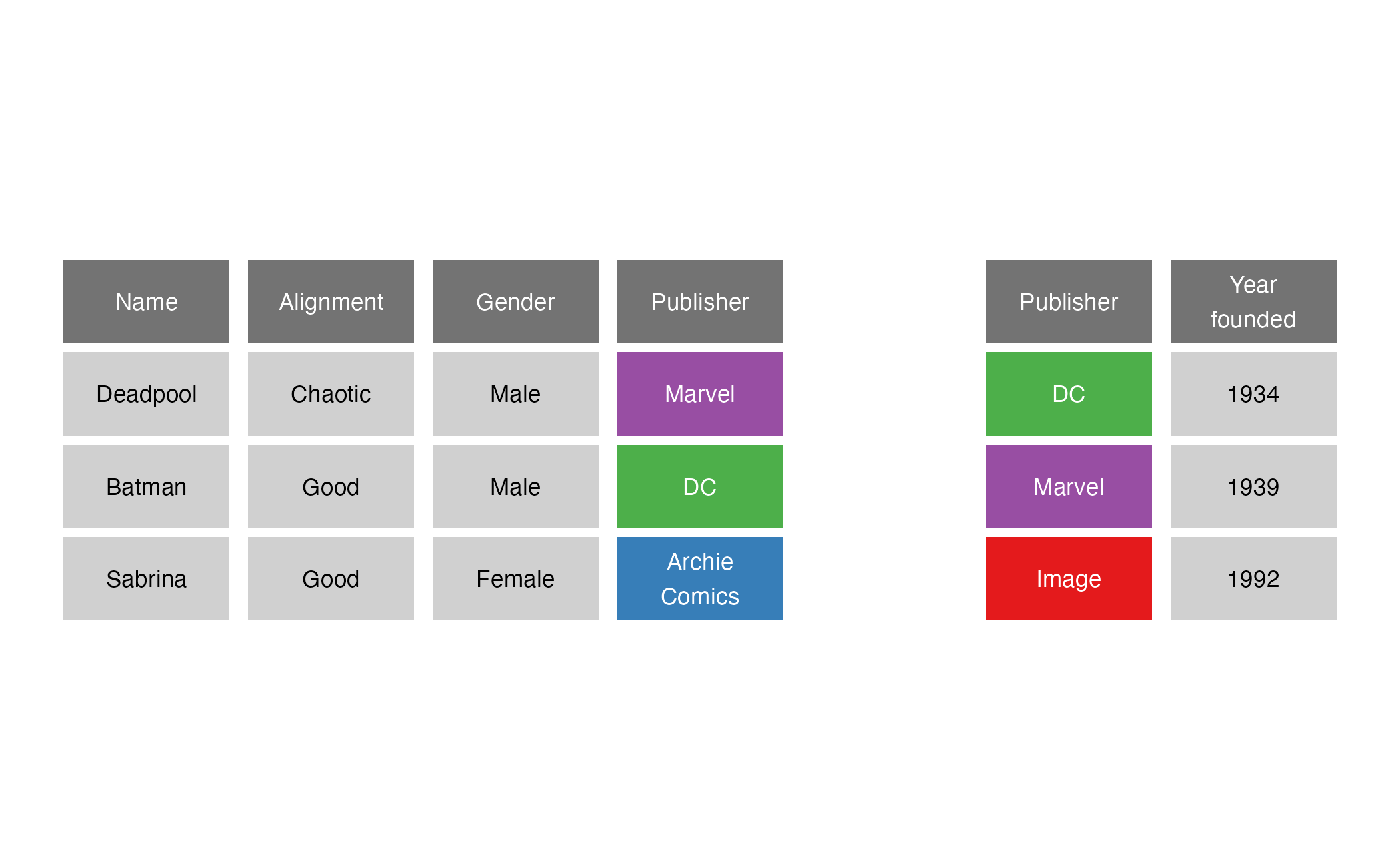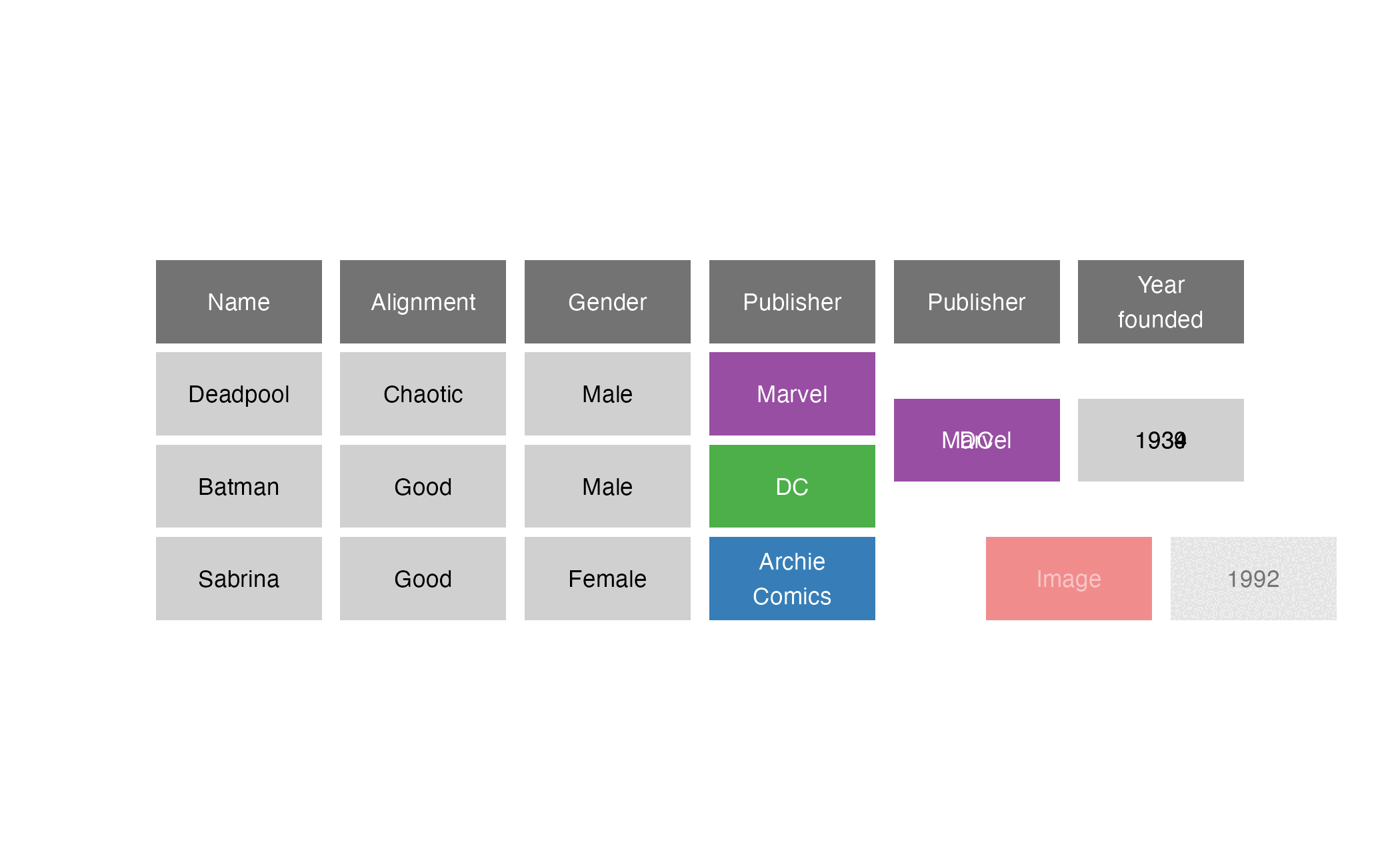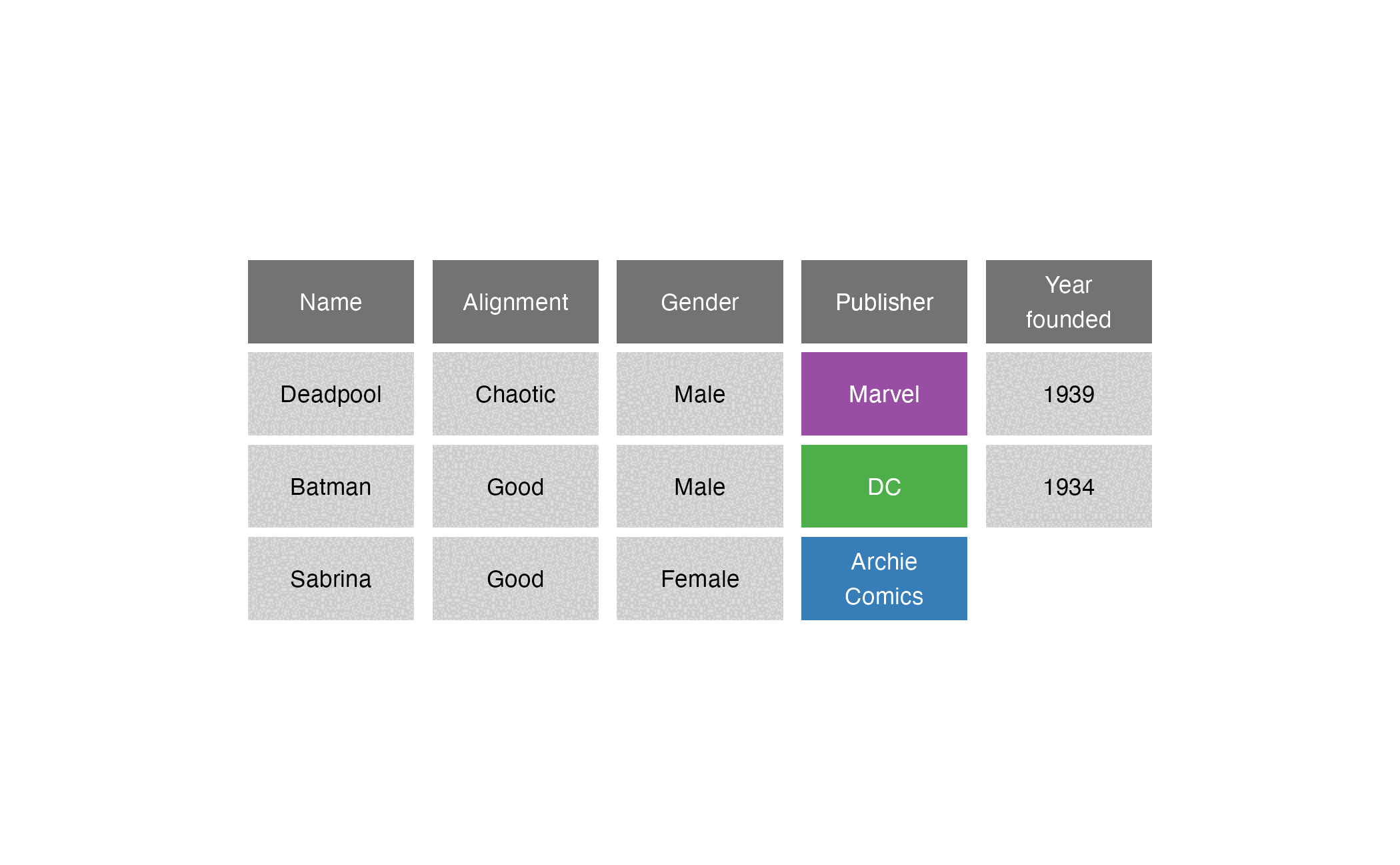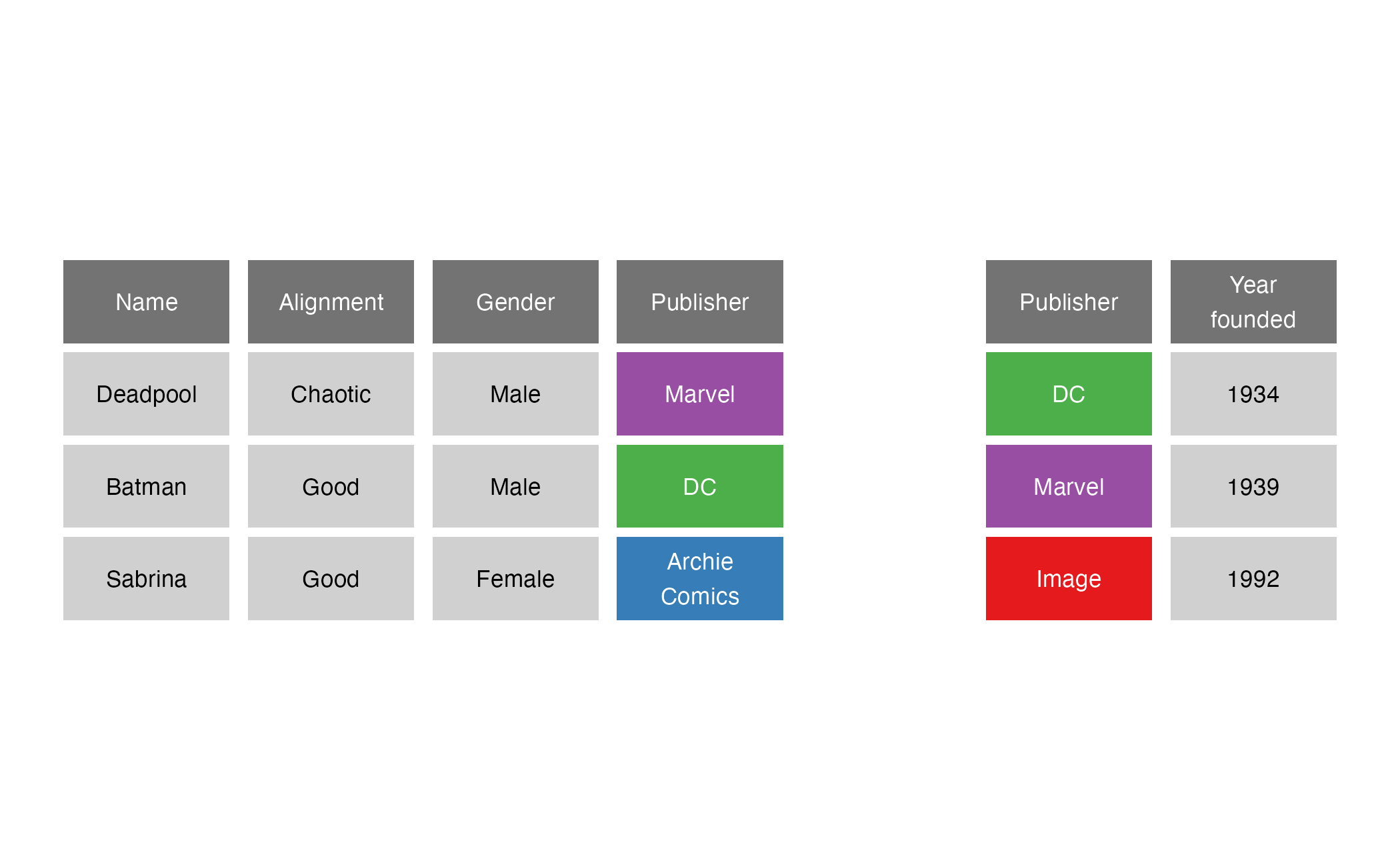
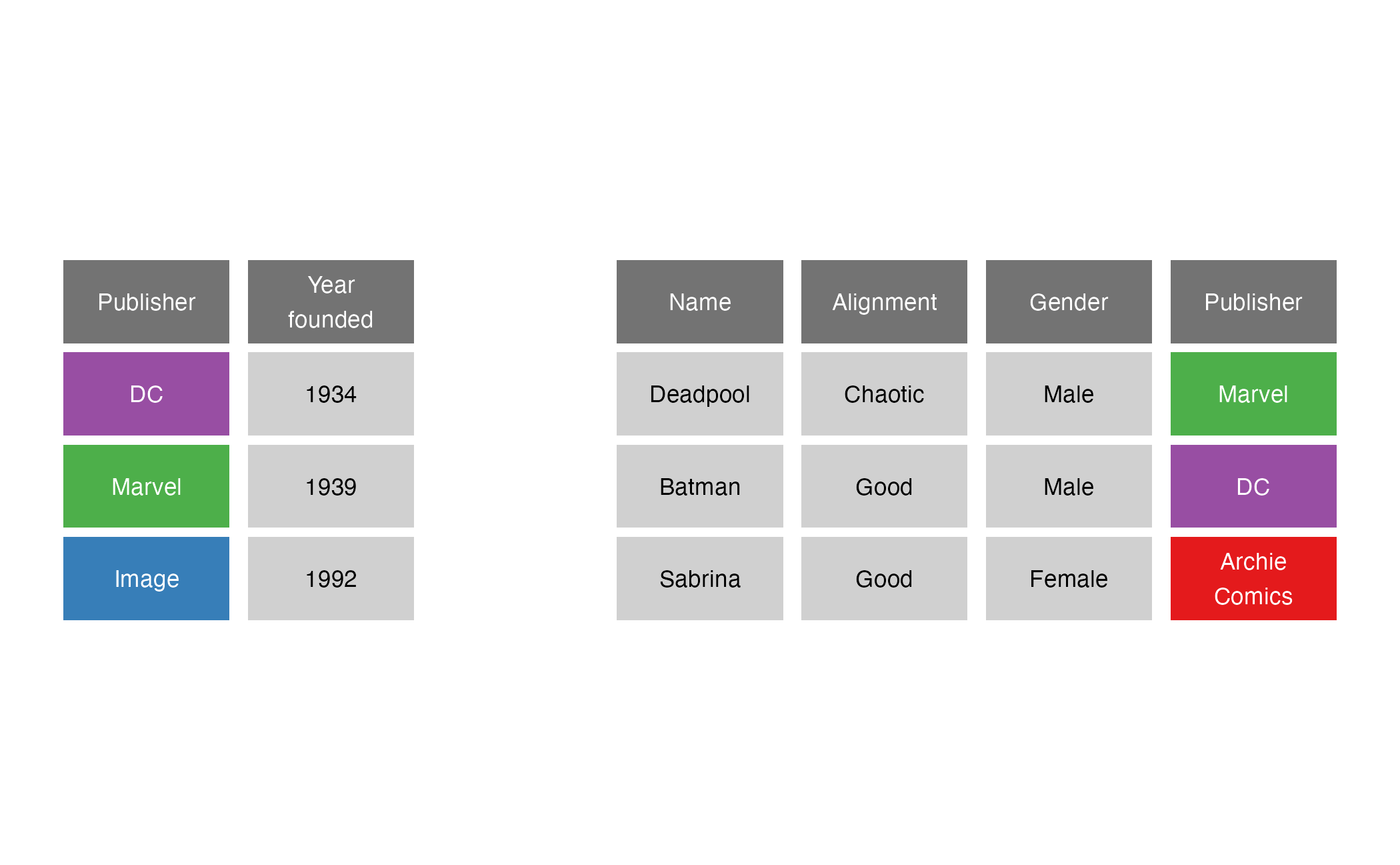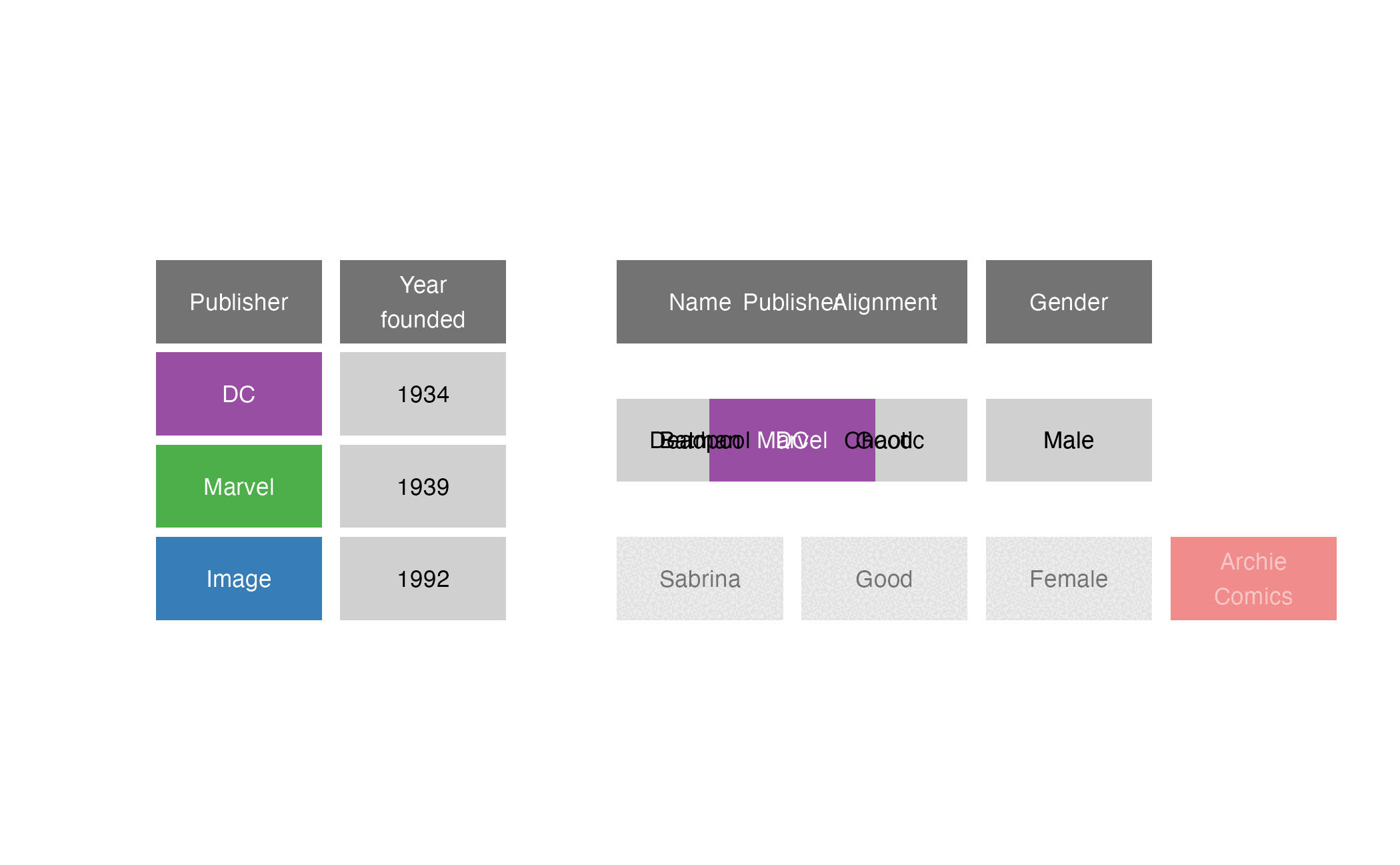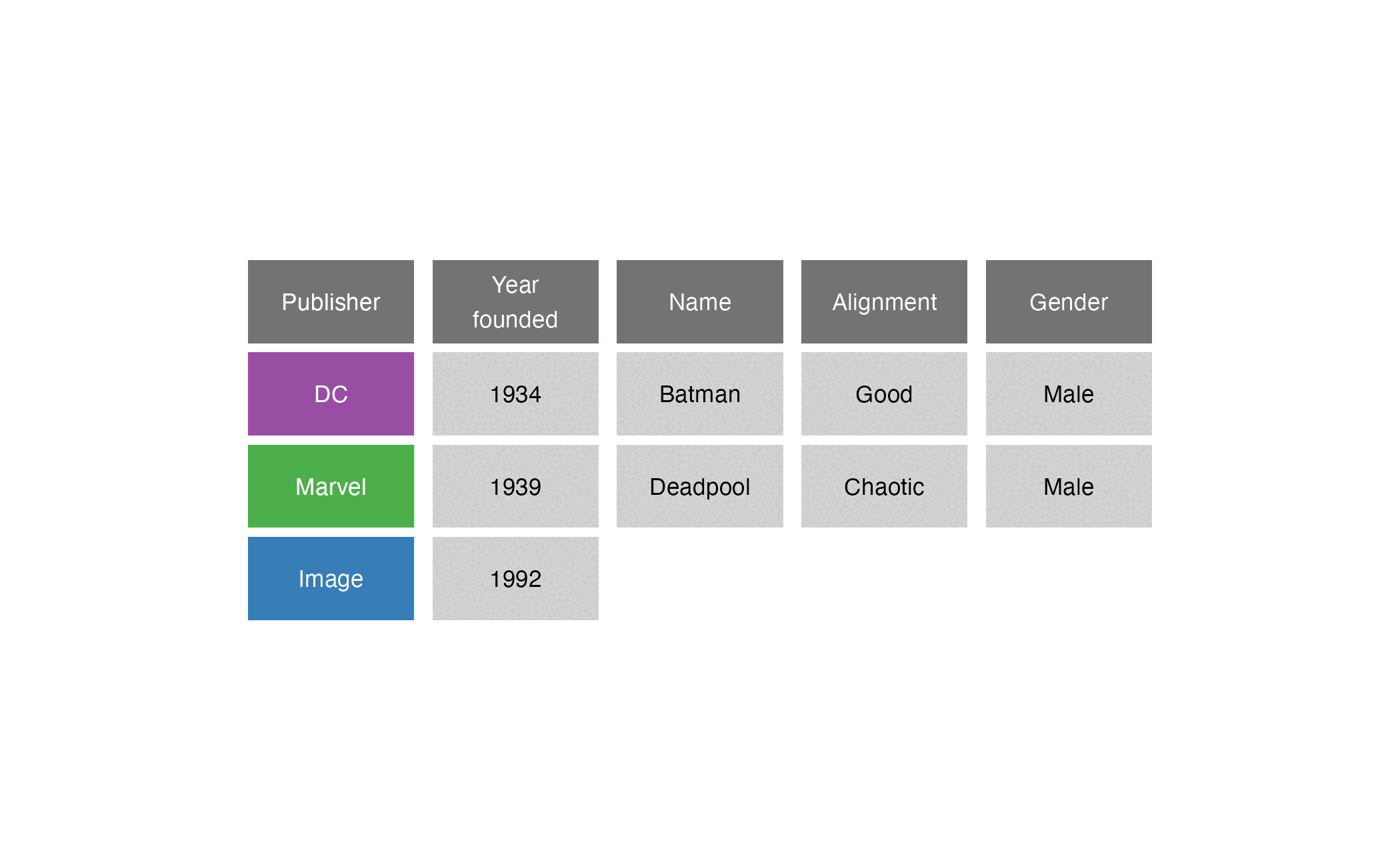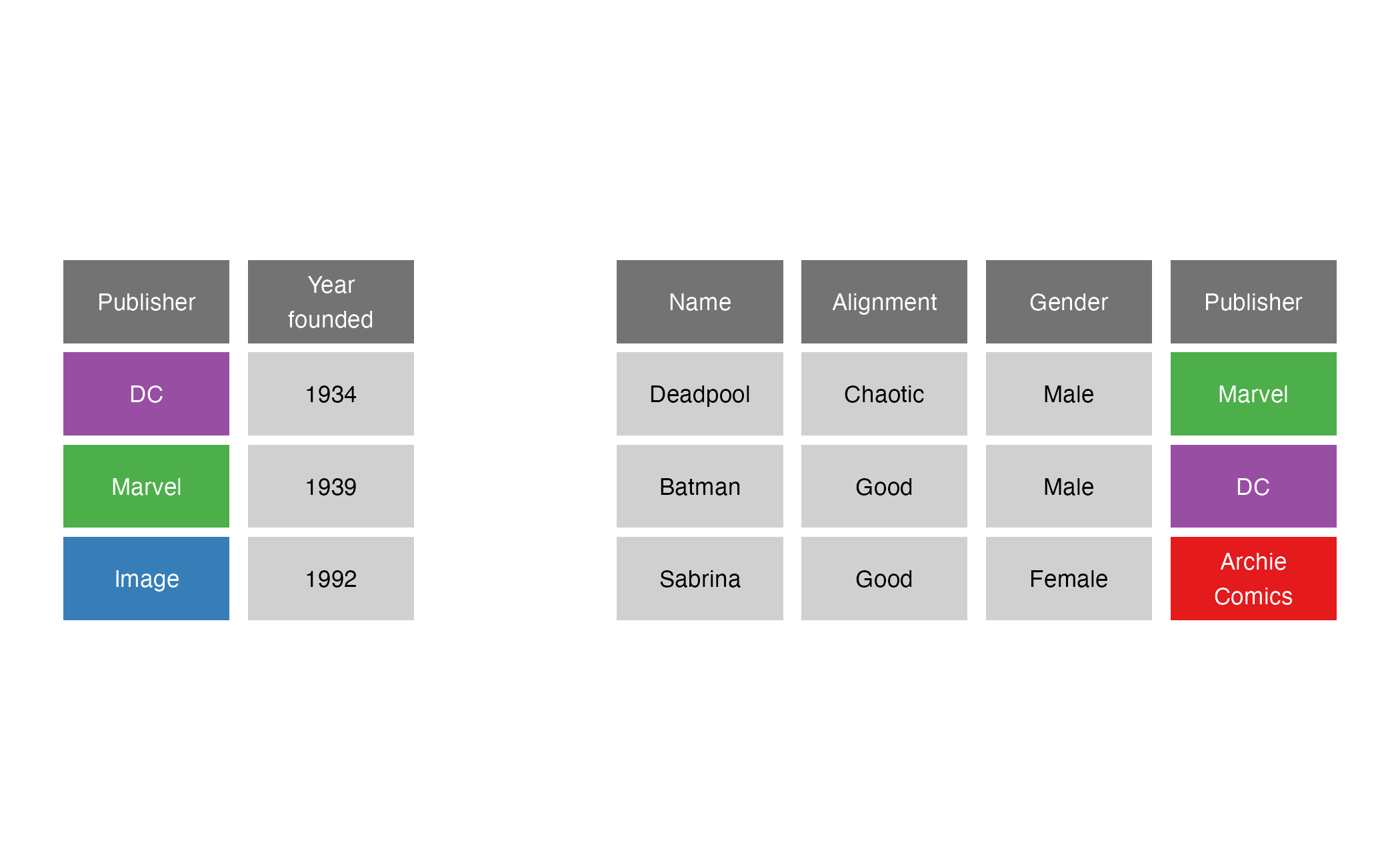
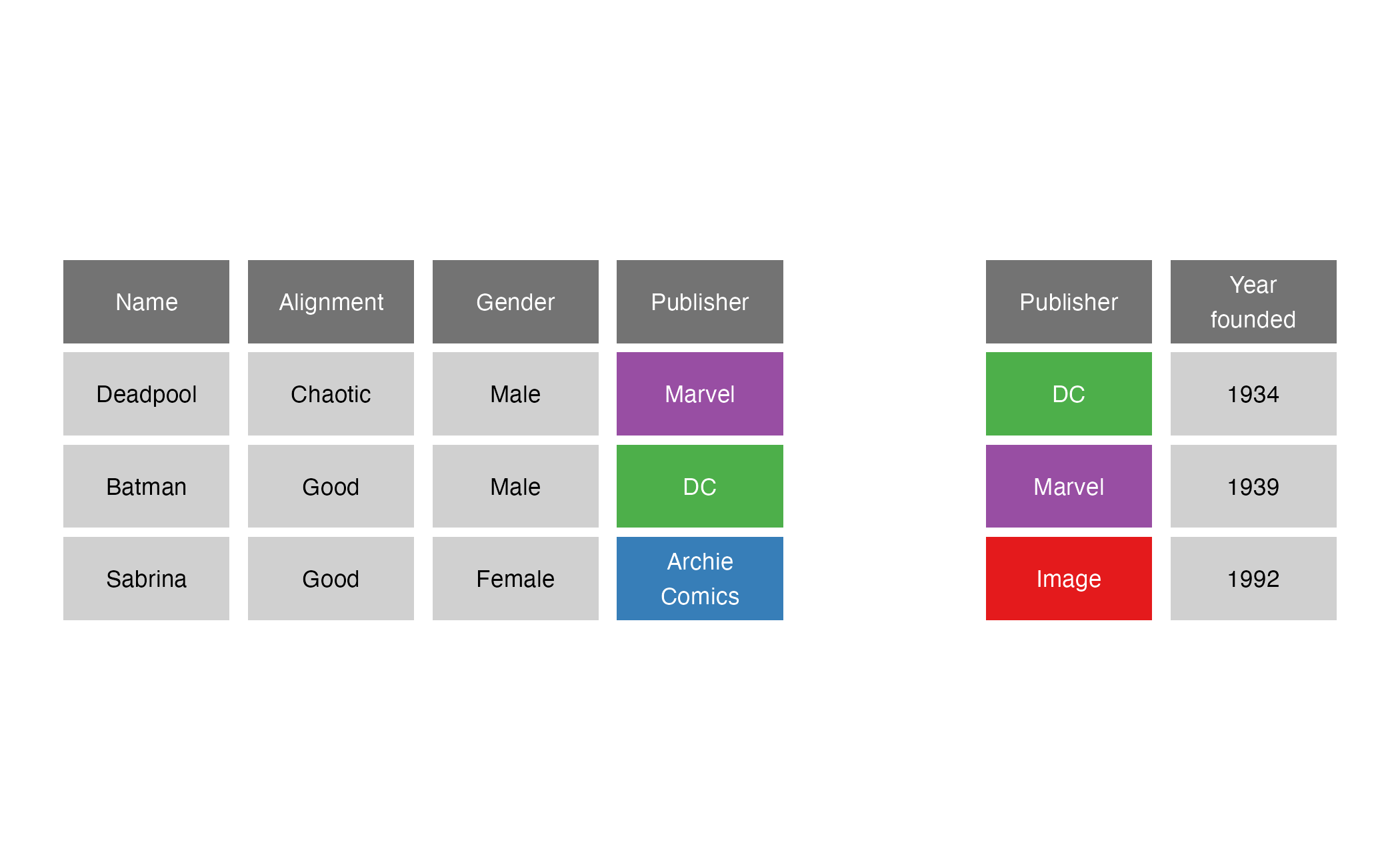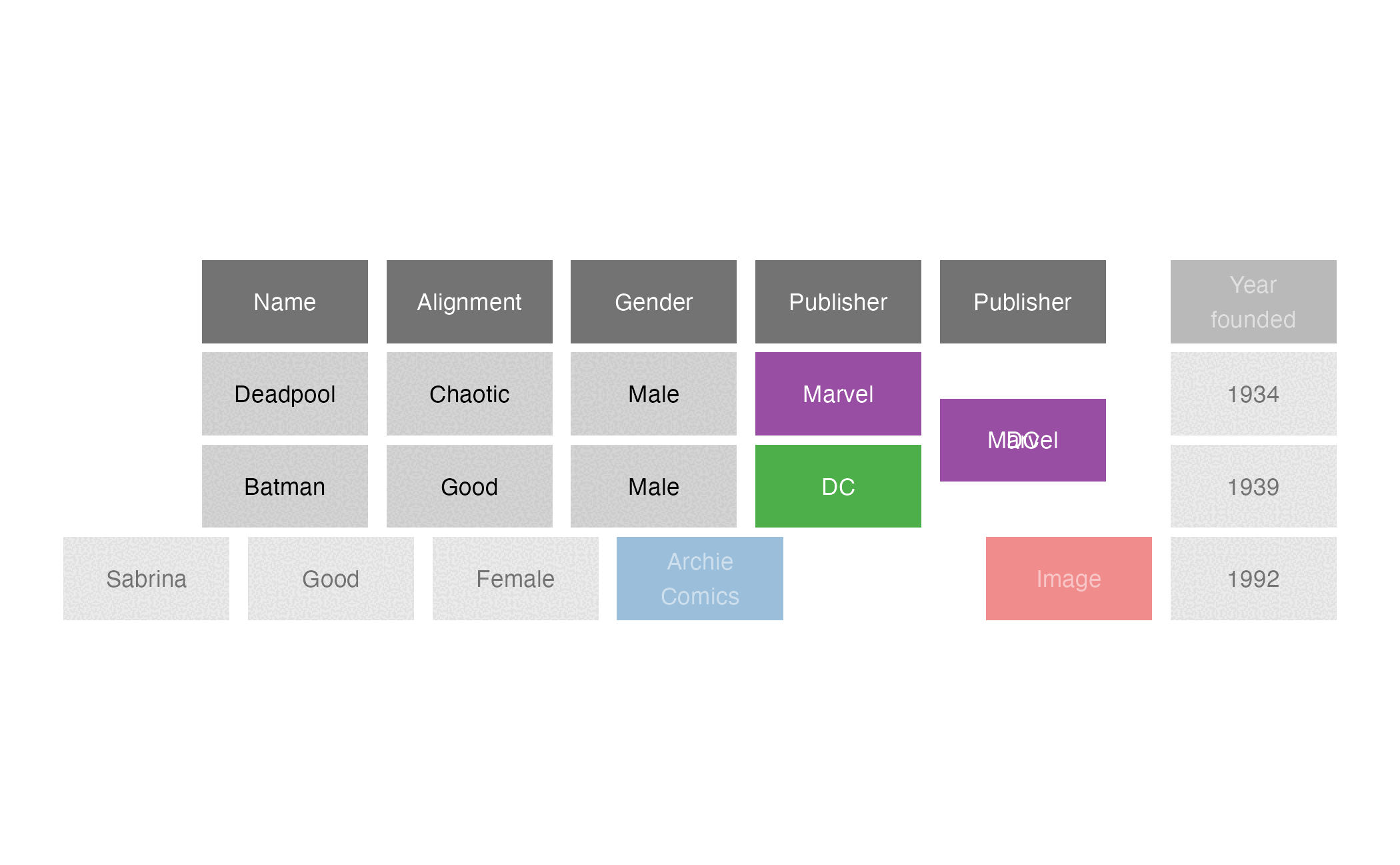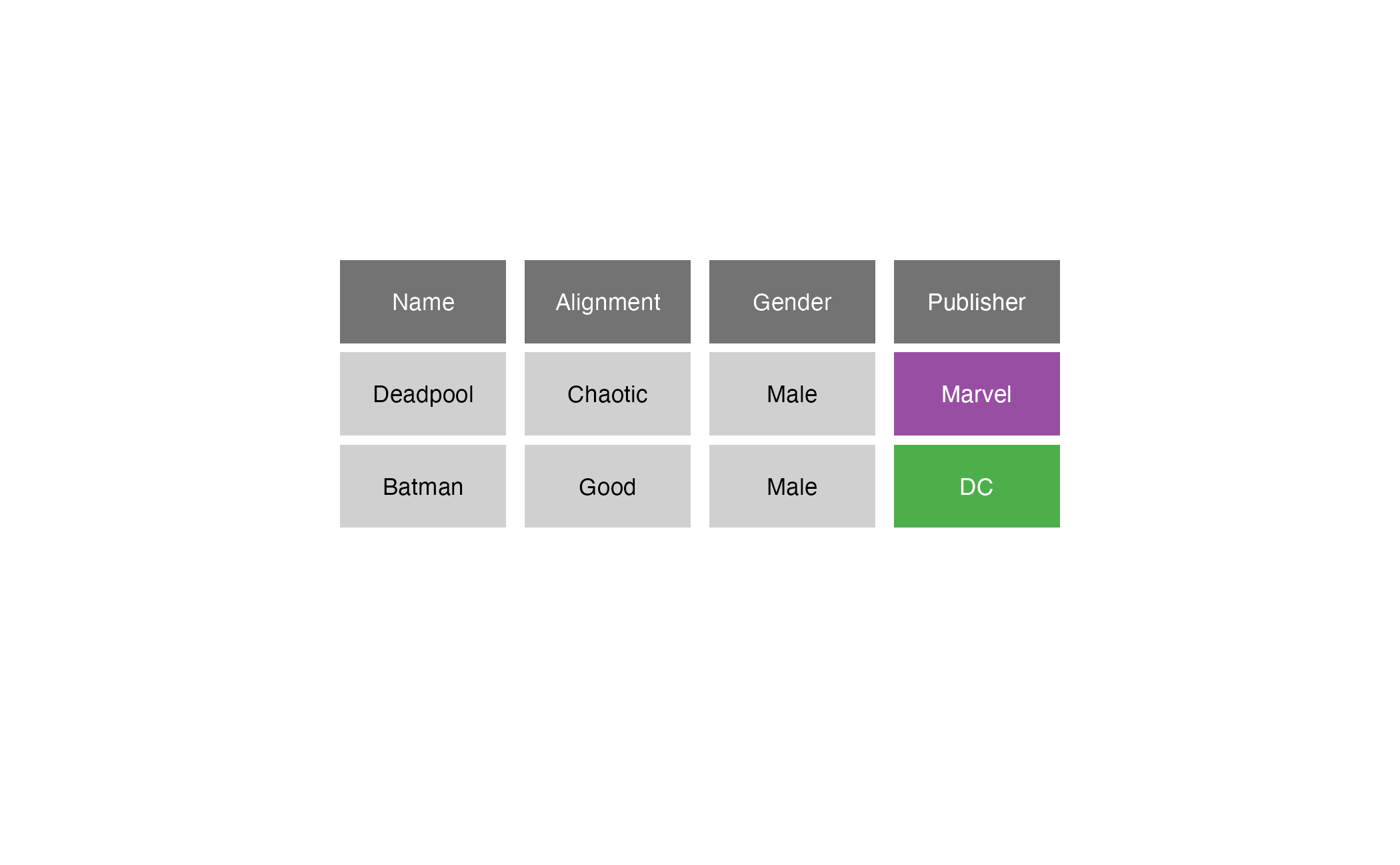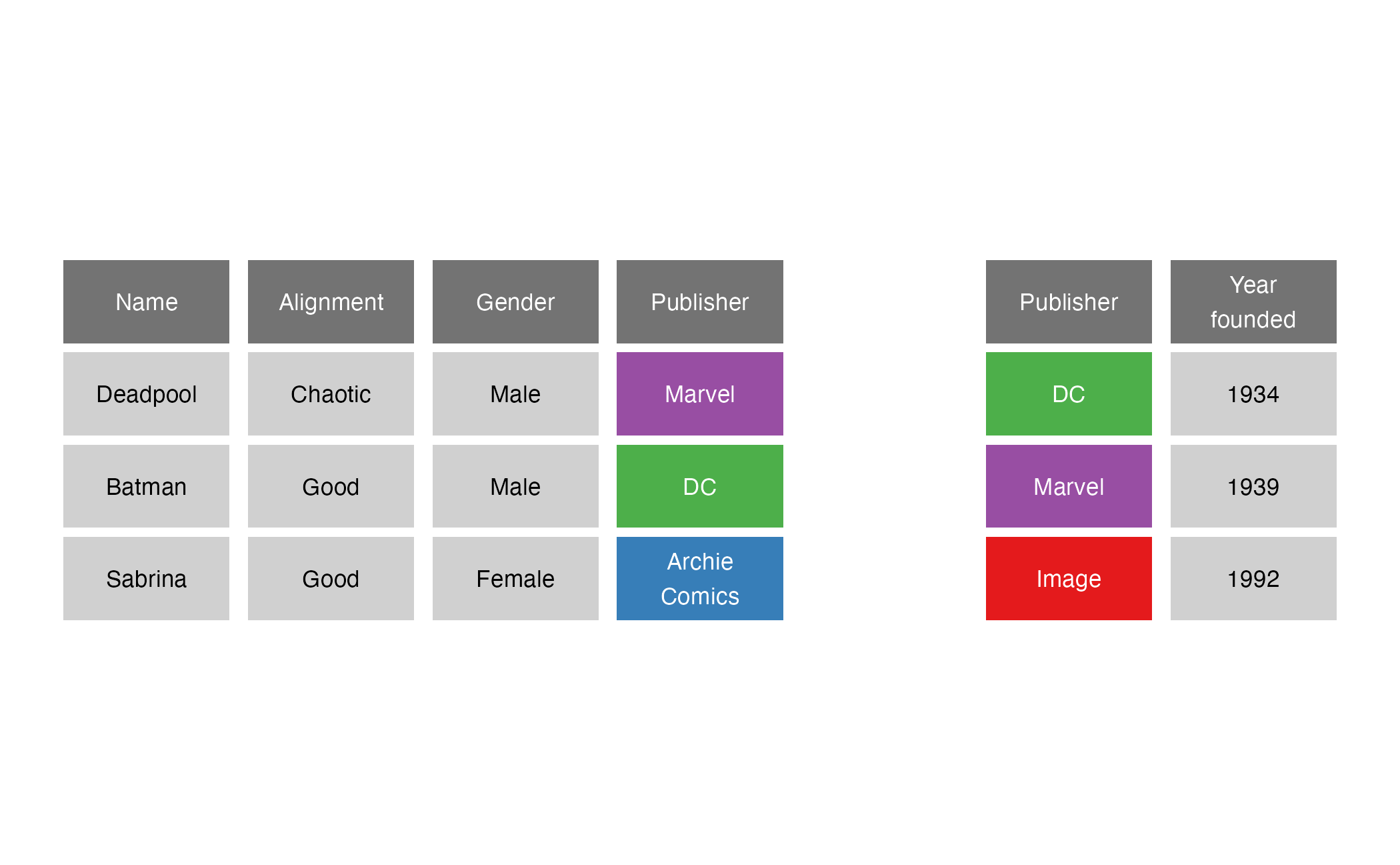
Comic book characters
| Name | Alignment | Gender | Publisher |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deadpool | Chaotic | Male | Marvel |
| Batman | Good | Male | DC |
| Sabrina | Good | Female | Archie Comics |
Publishers
| Publisher | Year founded |
|---|---|
| DC | 1934 |
| Marvel | 1939 |
| Image | 1992 |
Mutating joins
inner_join()
inner_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
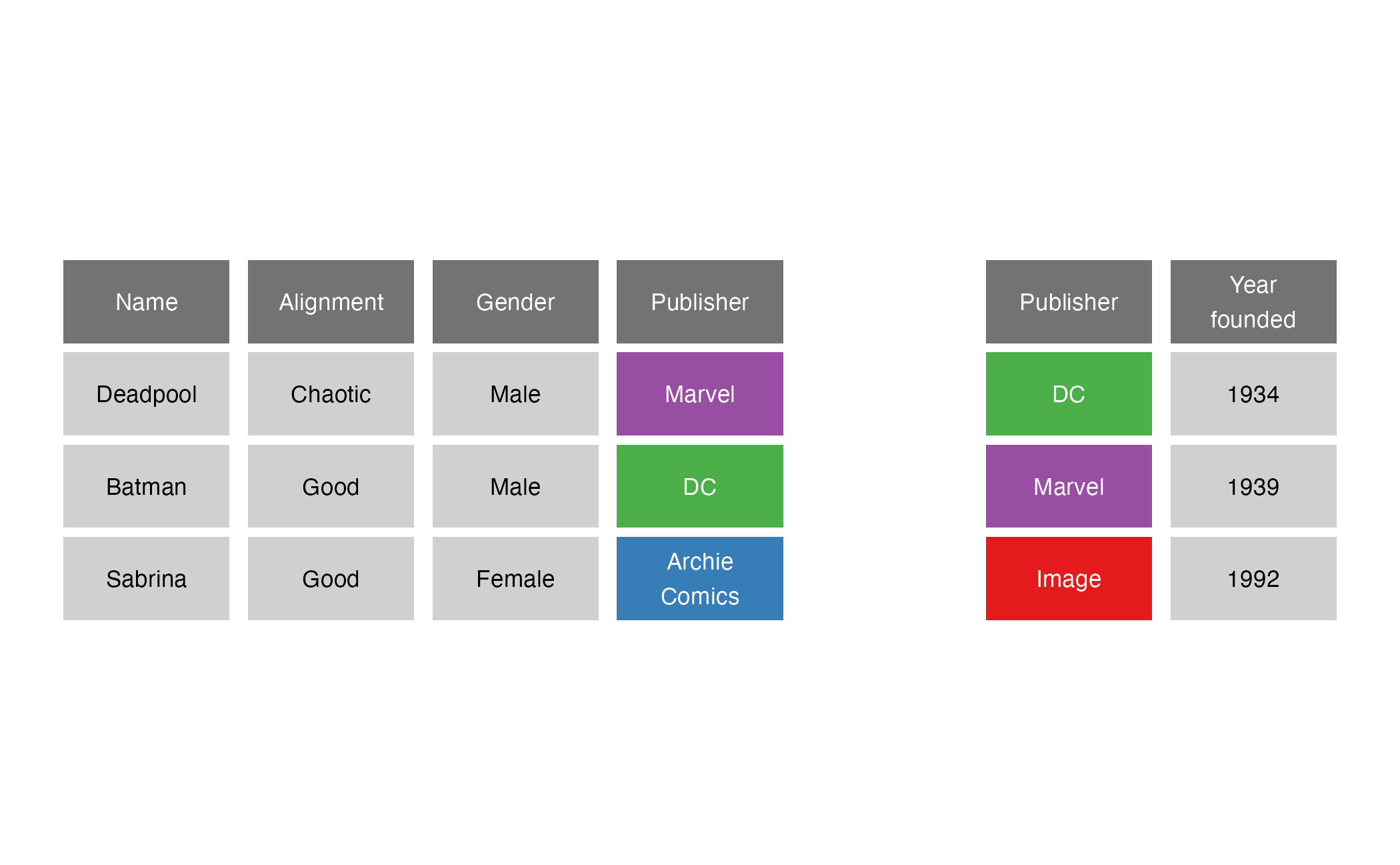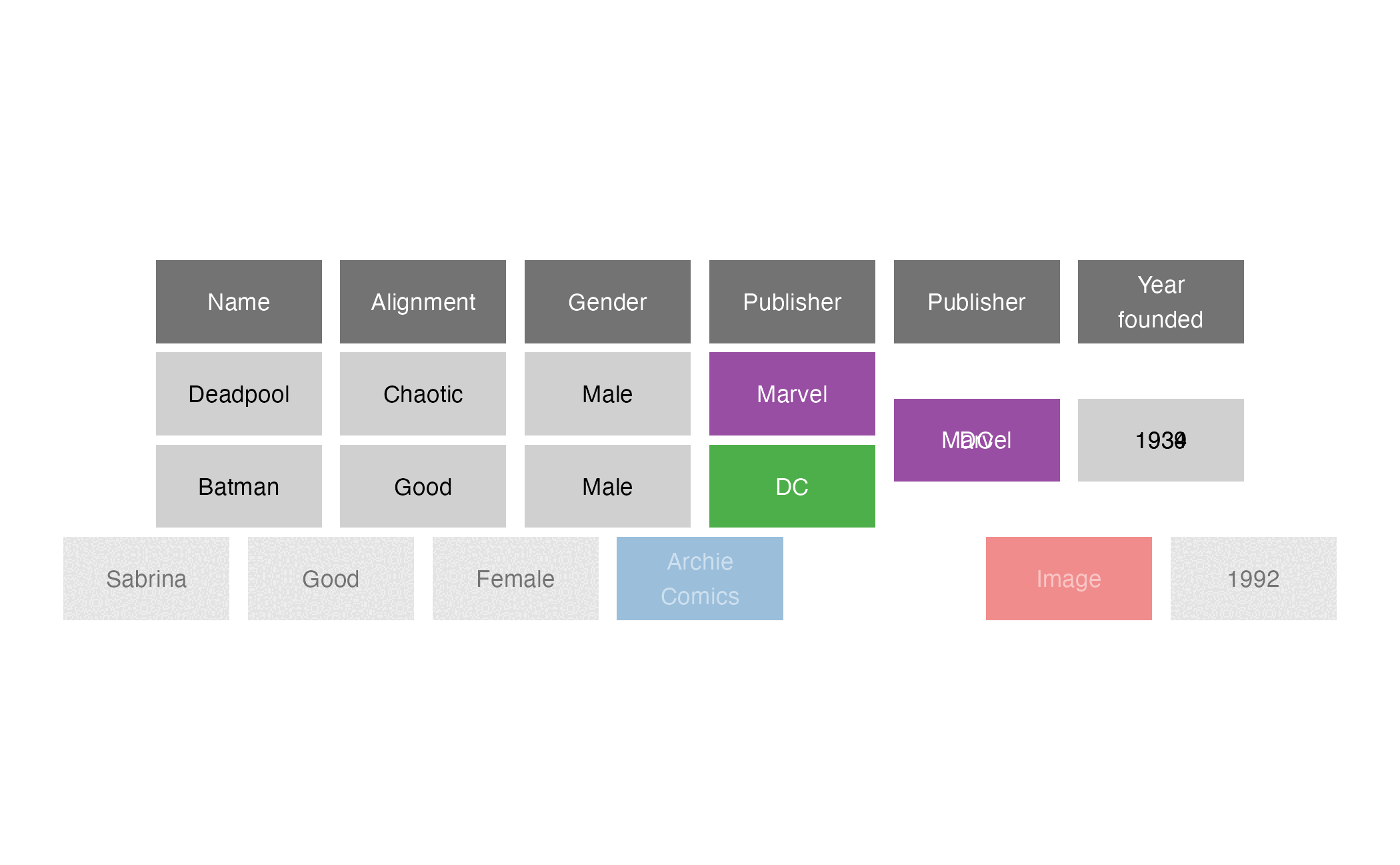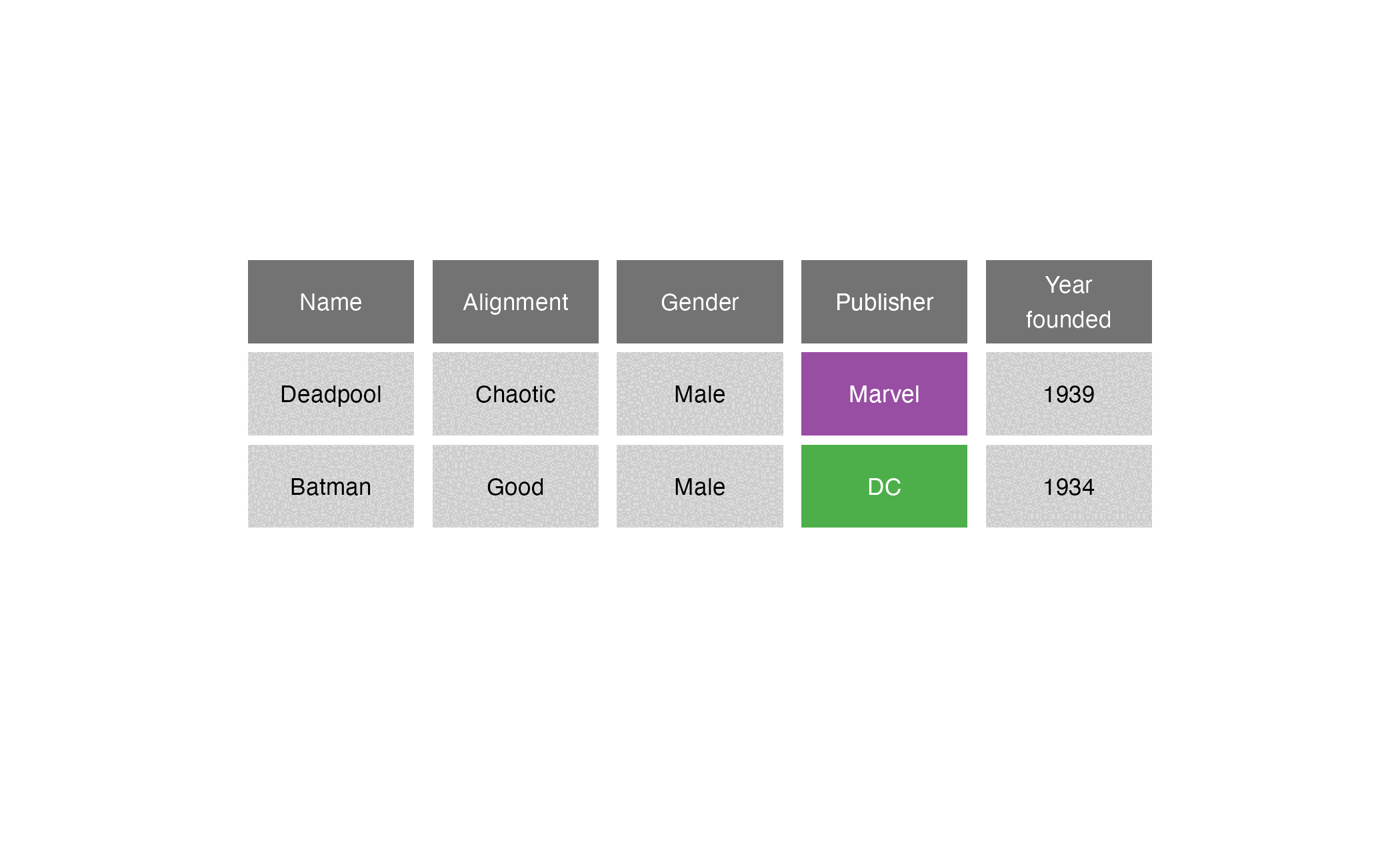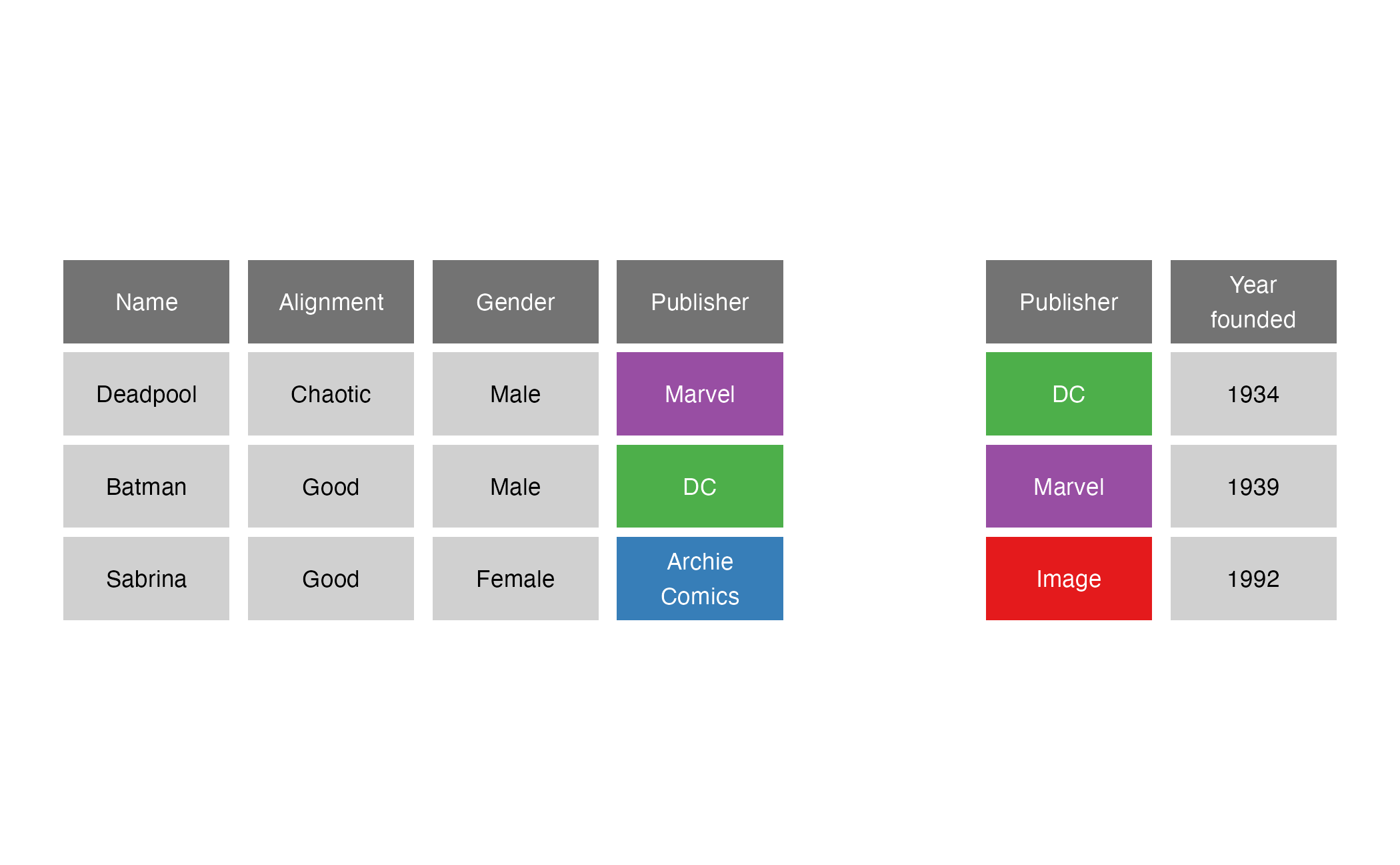
inner_join()
left_join()
left_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
left_join()
right_join()
right_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
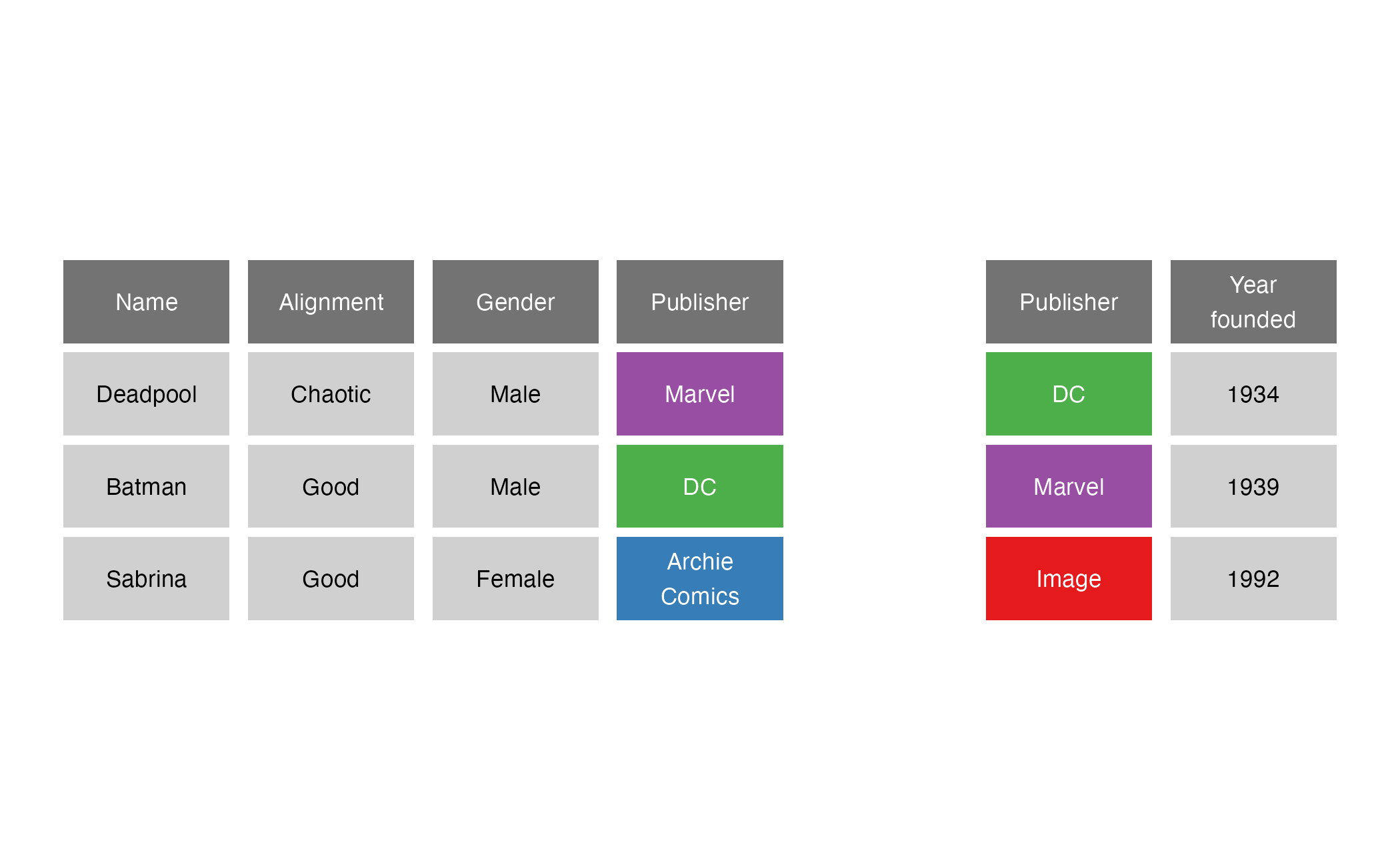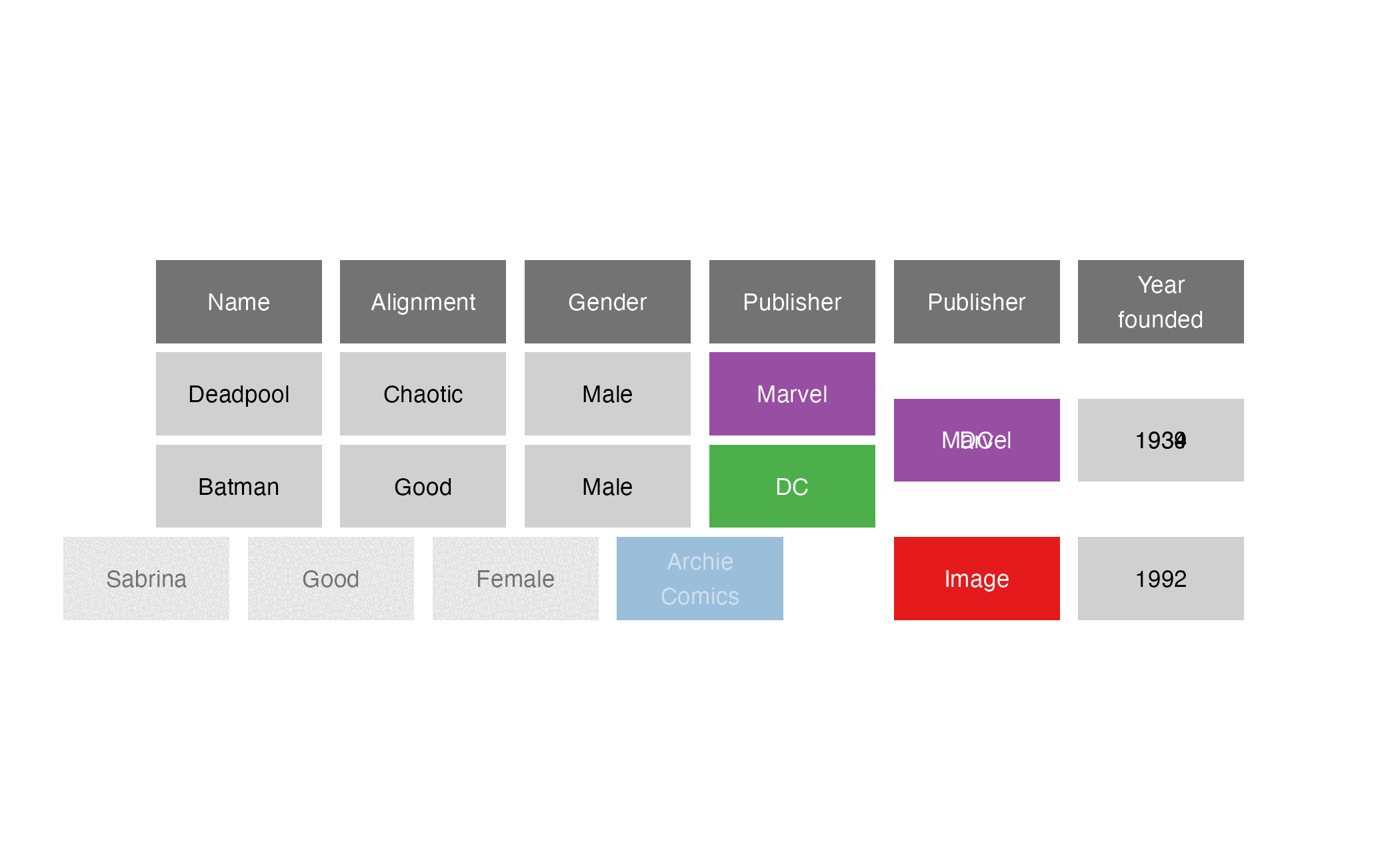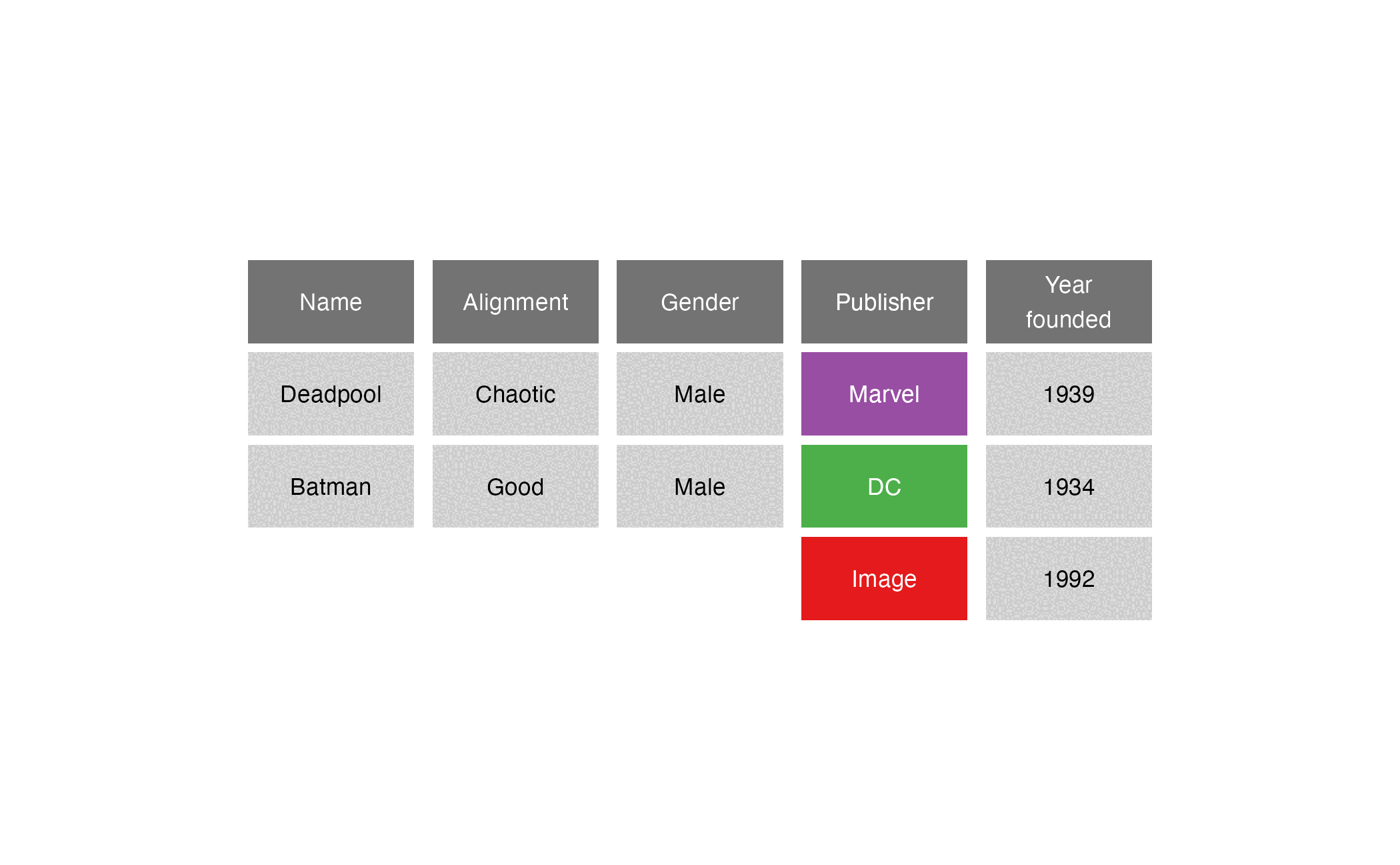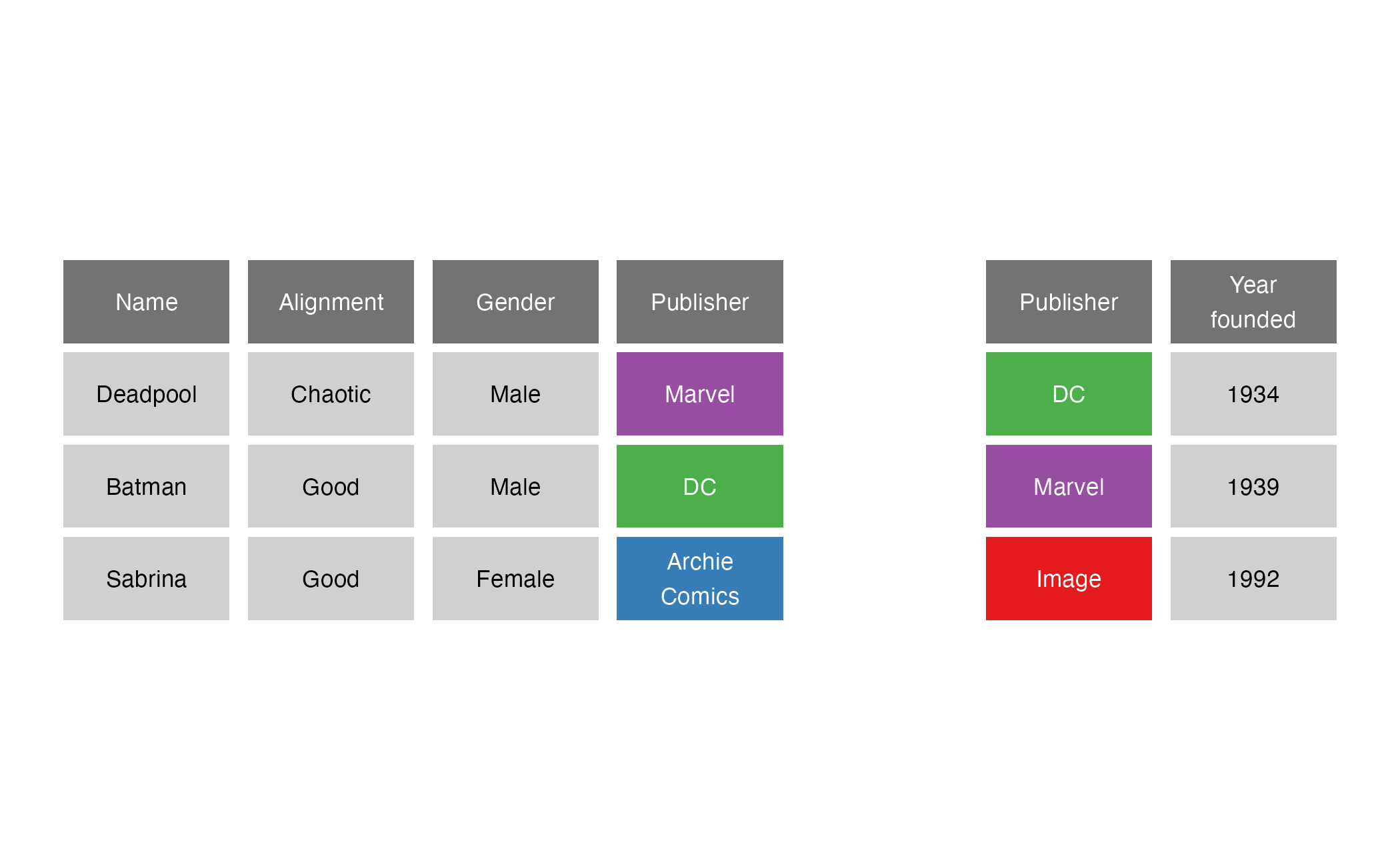
right_join()
right_join() reversed
left_join(x = publishers, y = superheroes, by = join_by(Publisher))
full_join()
full_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
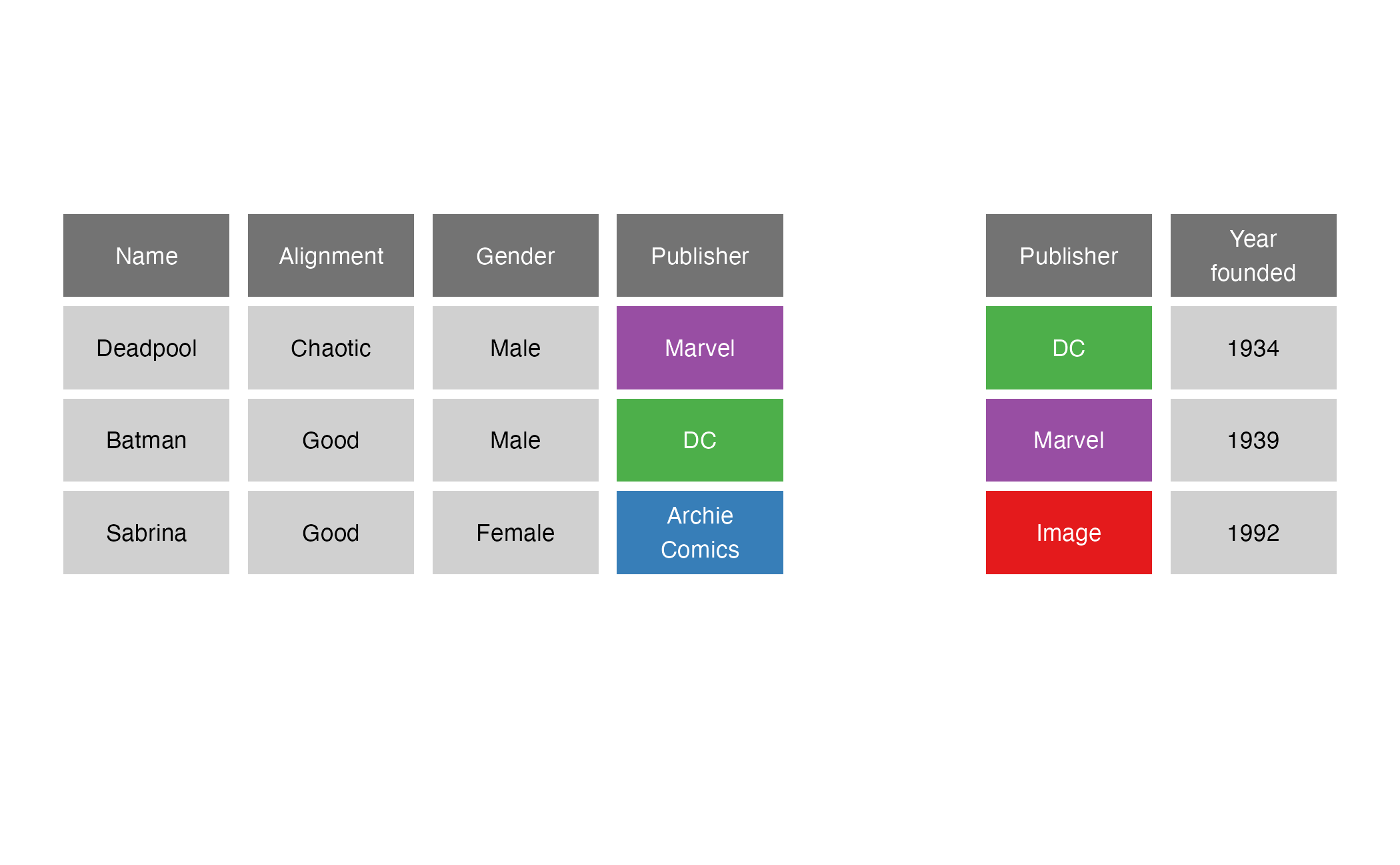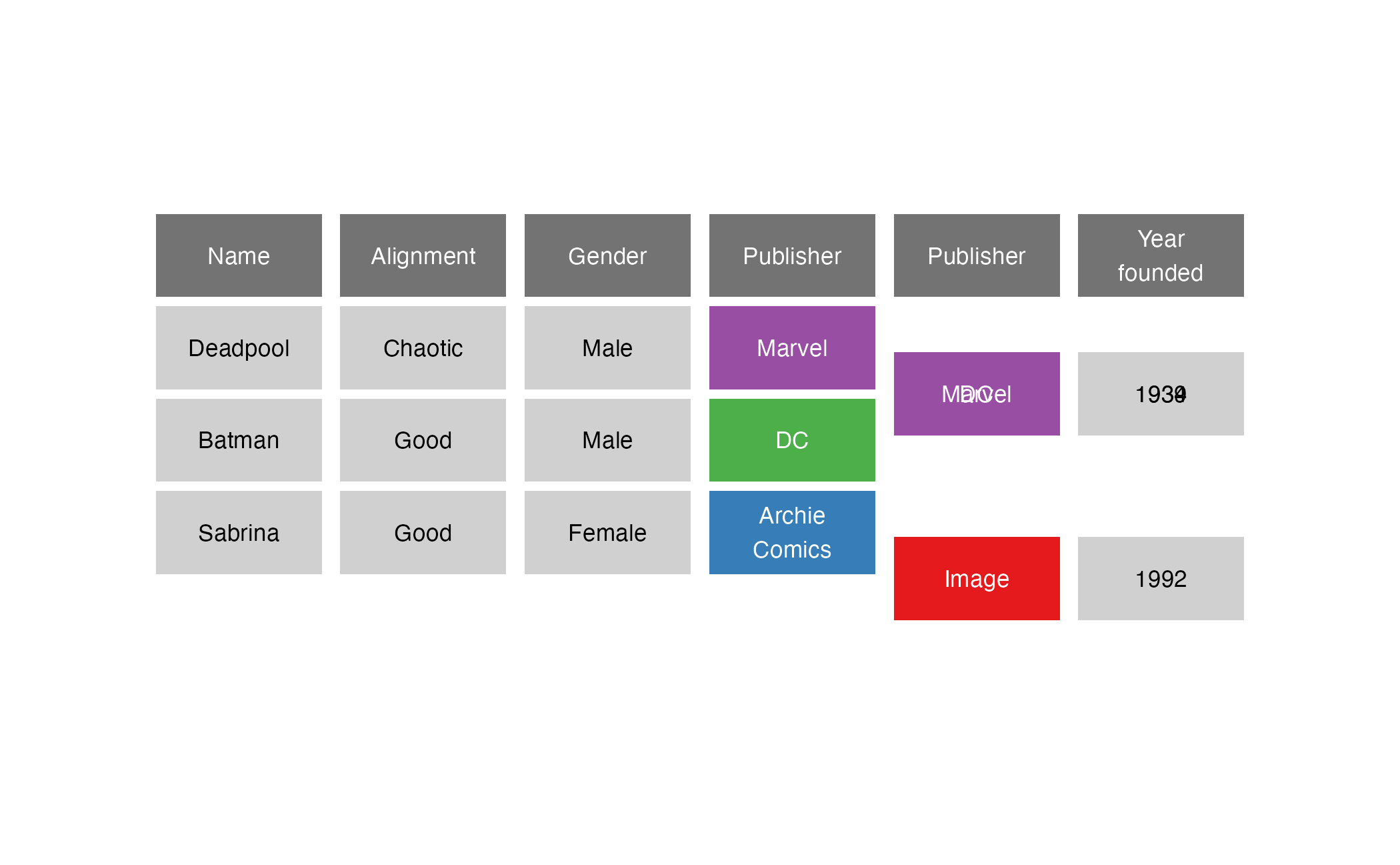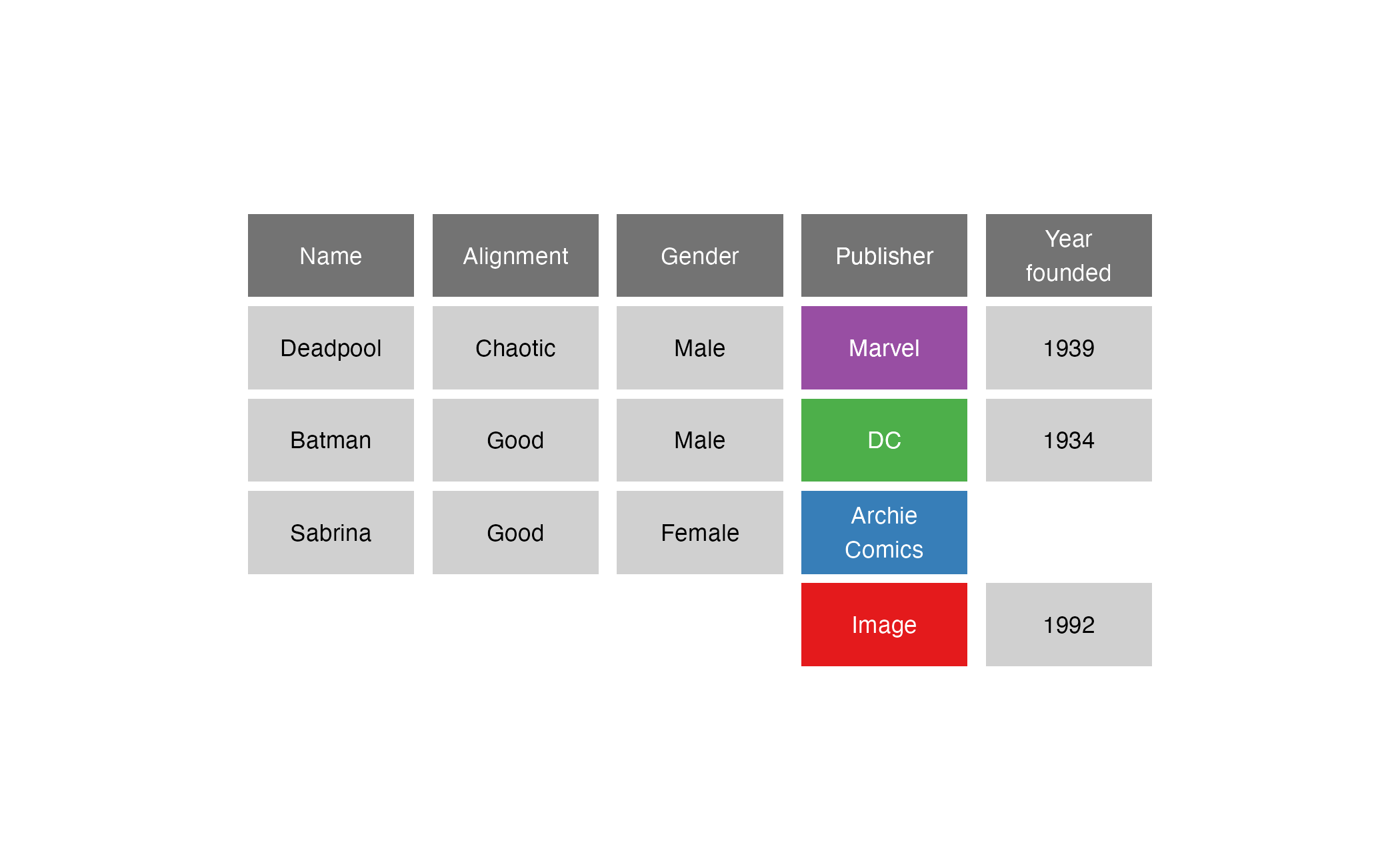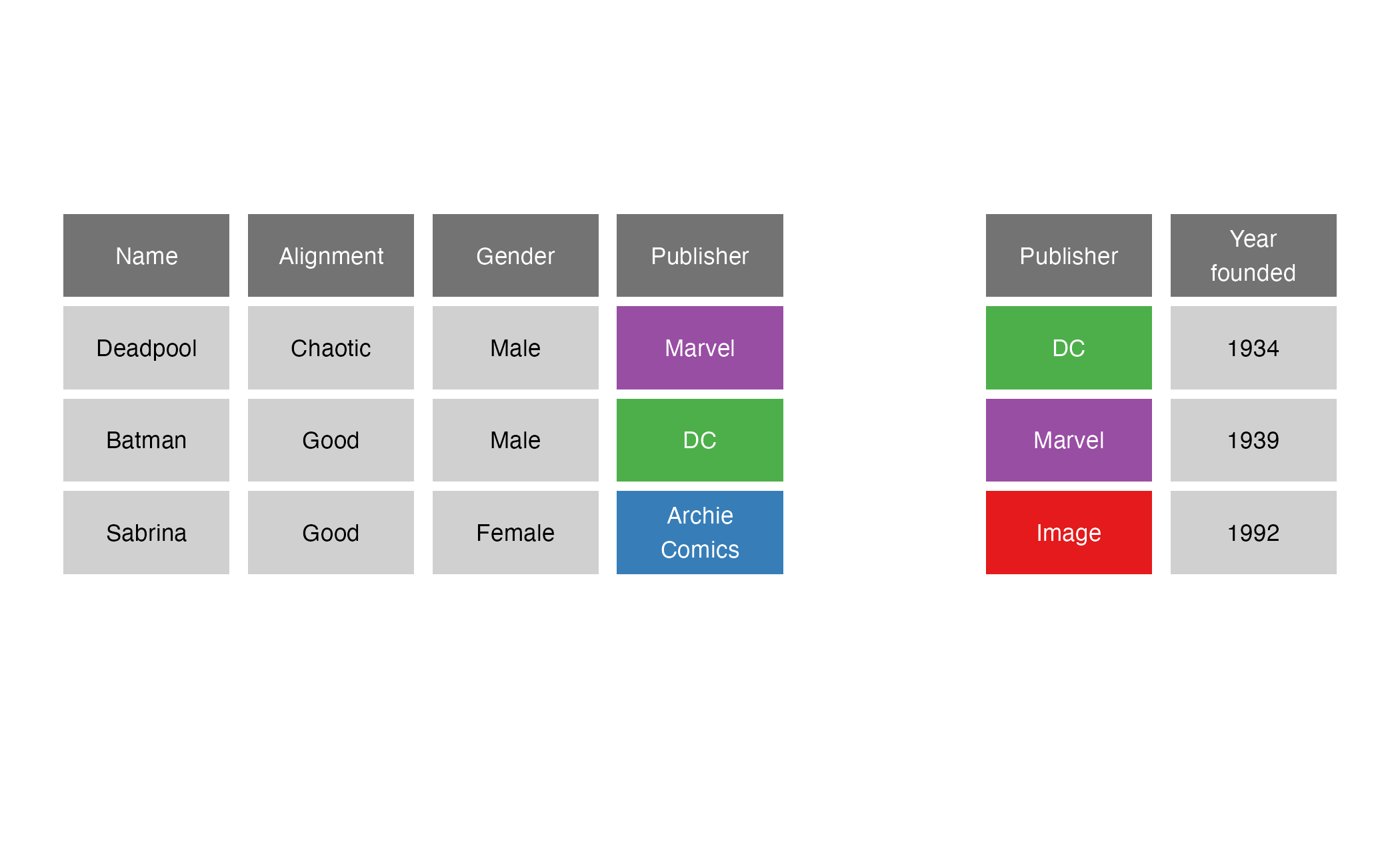
full_join()
# A tibble: 4 × 5
Name Alignment Gender Publisher `Year\nfounded`
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Deadpool Chaotic Male "Marvel" 1939
2 Batman Good Male "DC" 1934
3 Sabrina Good Female "Archie\nComics" NA
4 <NA> <NA> <NA> "Image" 1992Filtering joins
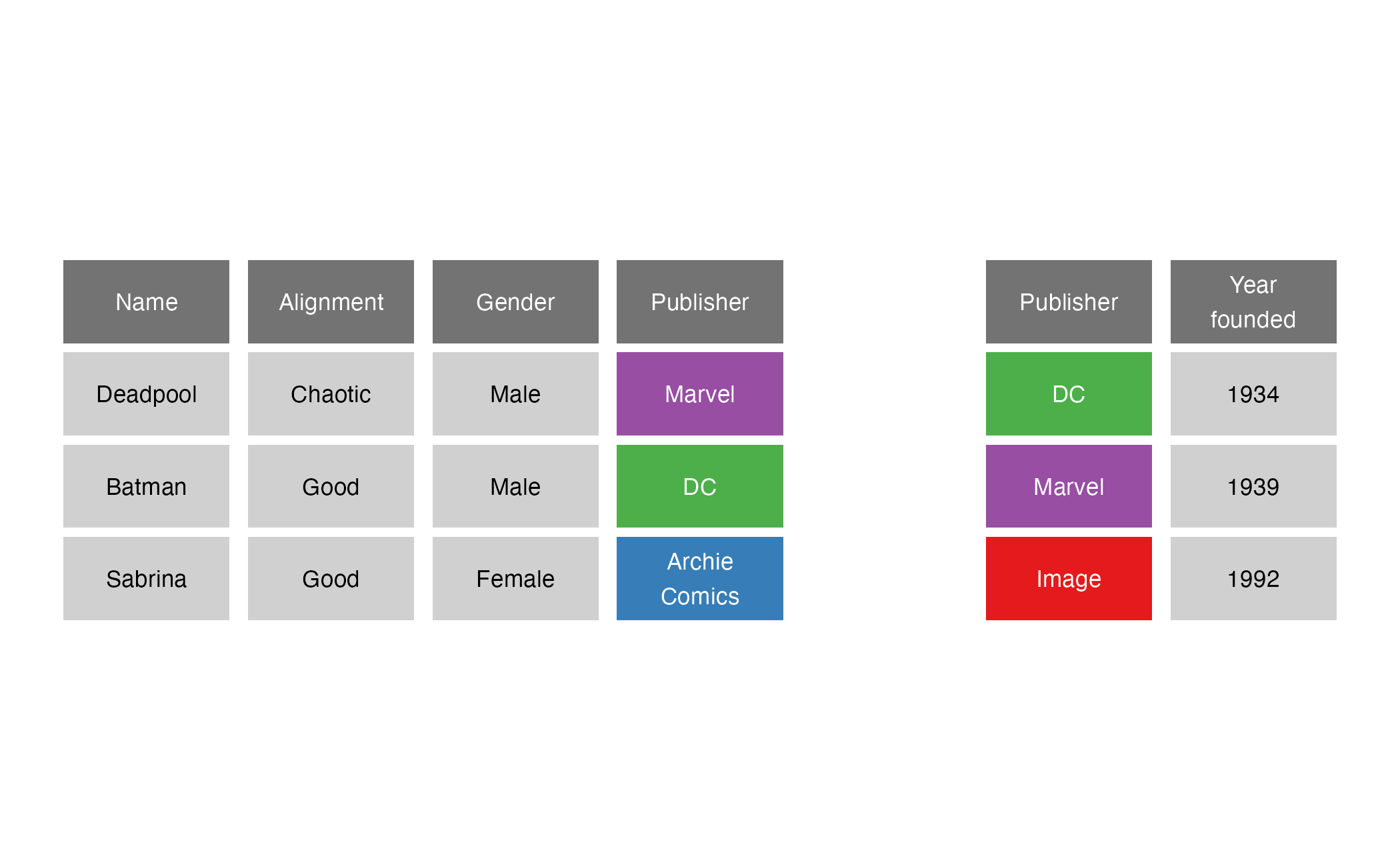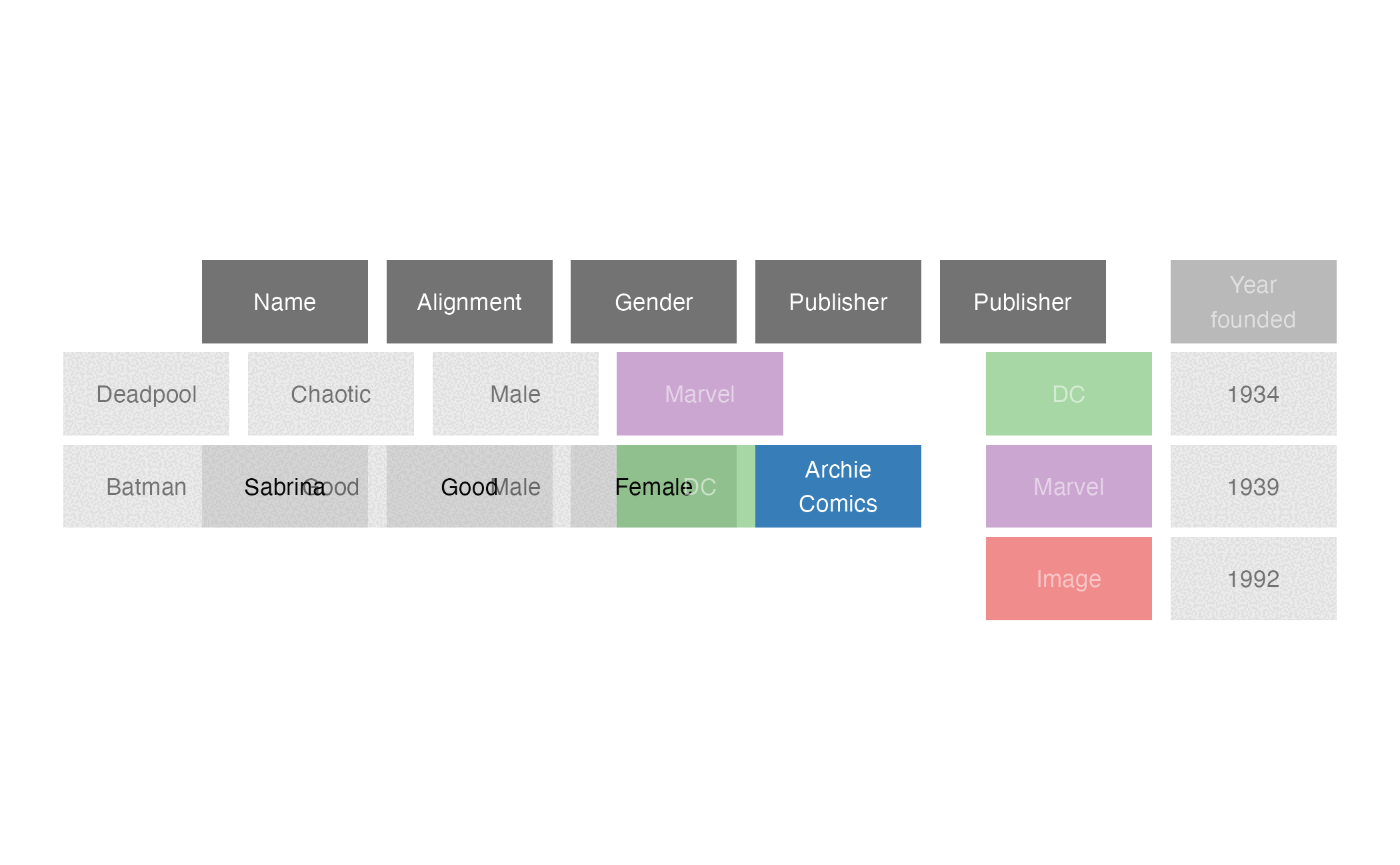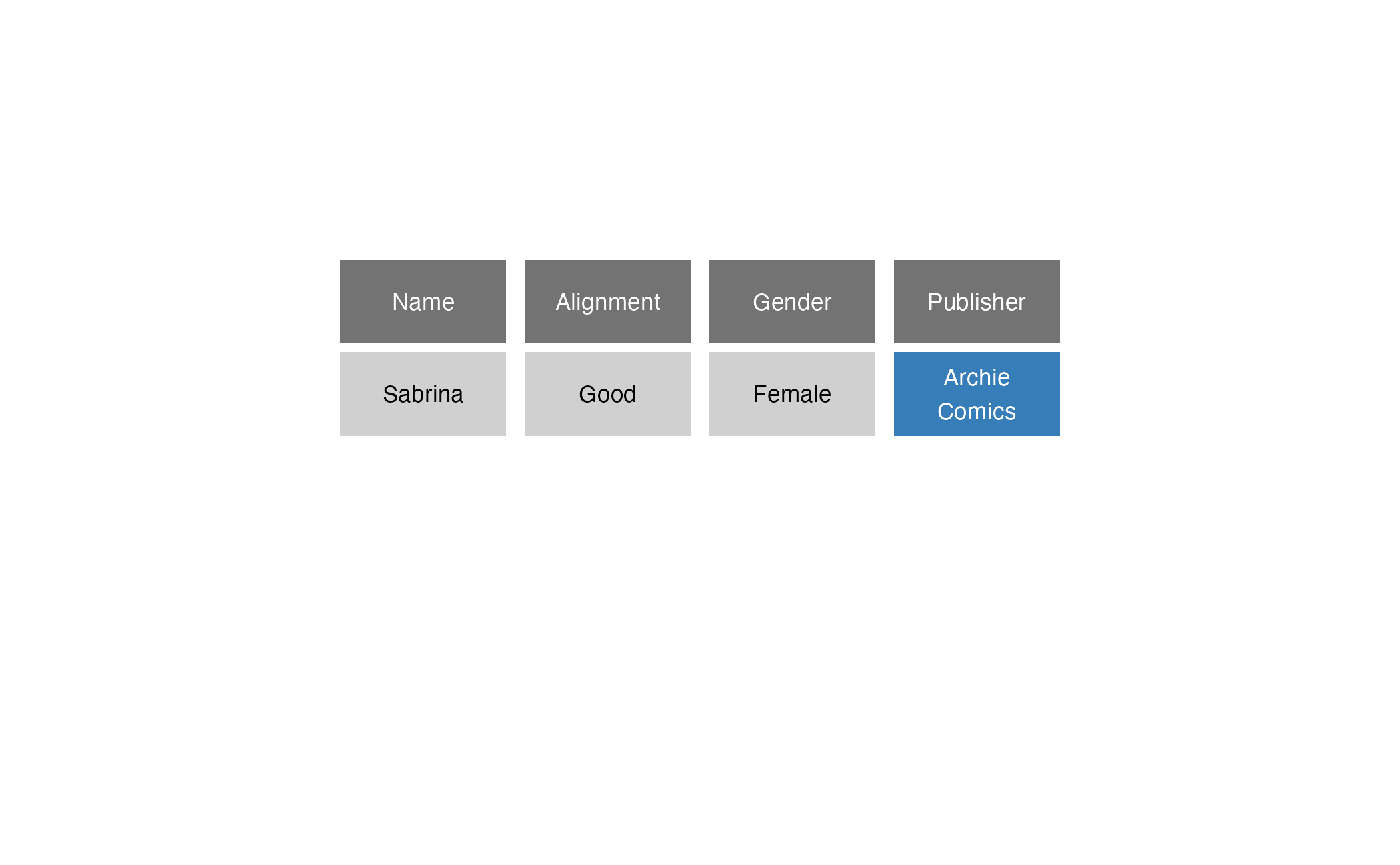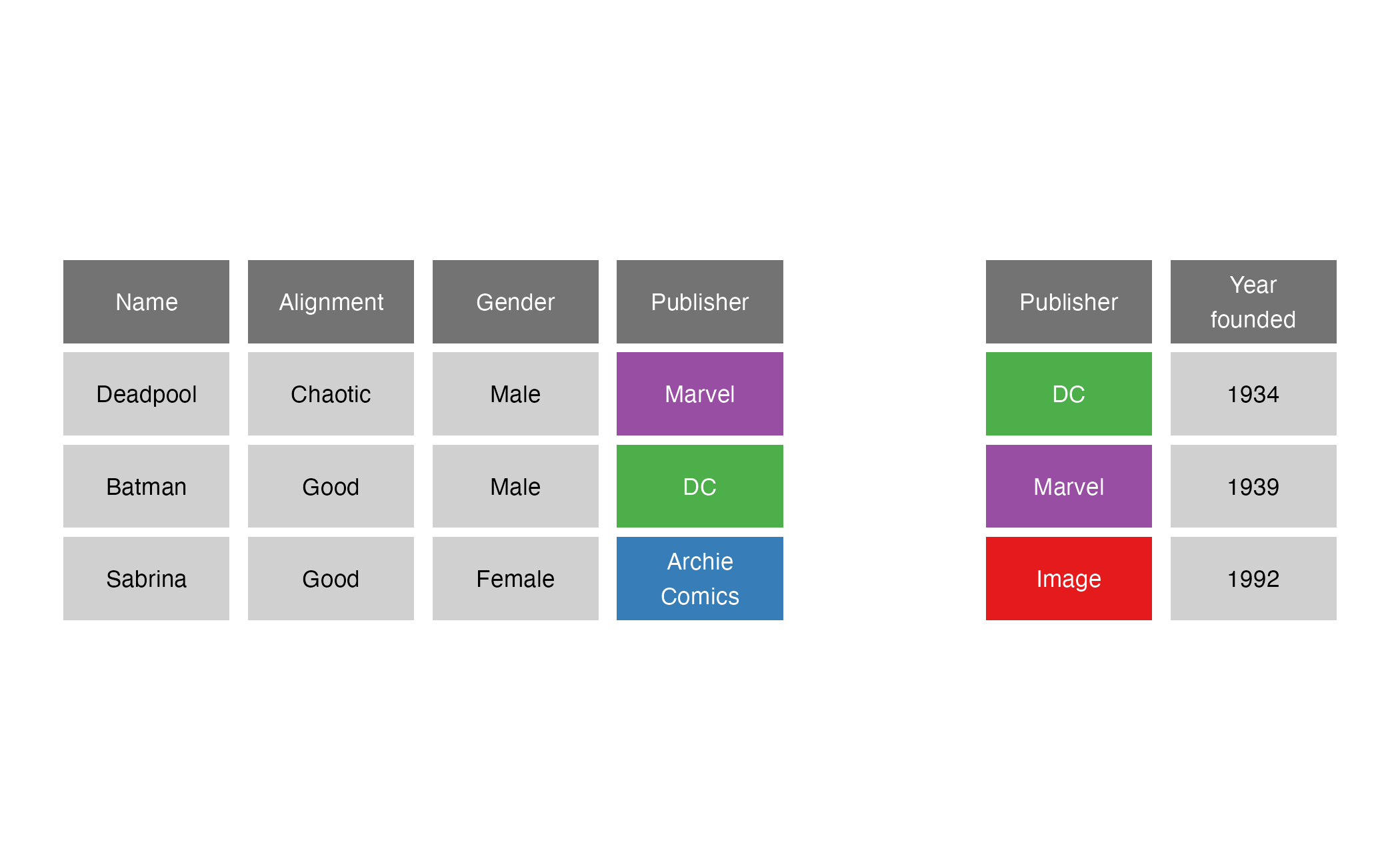
semi_join()
semi_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
semi_join()
anti_join()
anti_join(x = superheroes, y = publishers, by = join_by(Publisher))
anti_join()
Application exercise
Goal
Instructions
Join data from multiple data frames, summarize it, and create this plot.
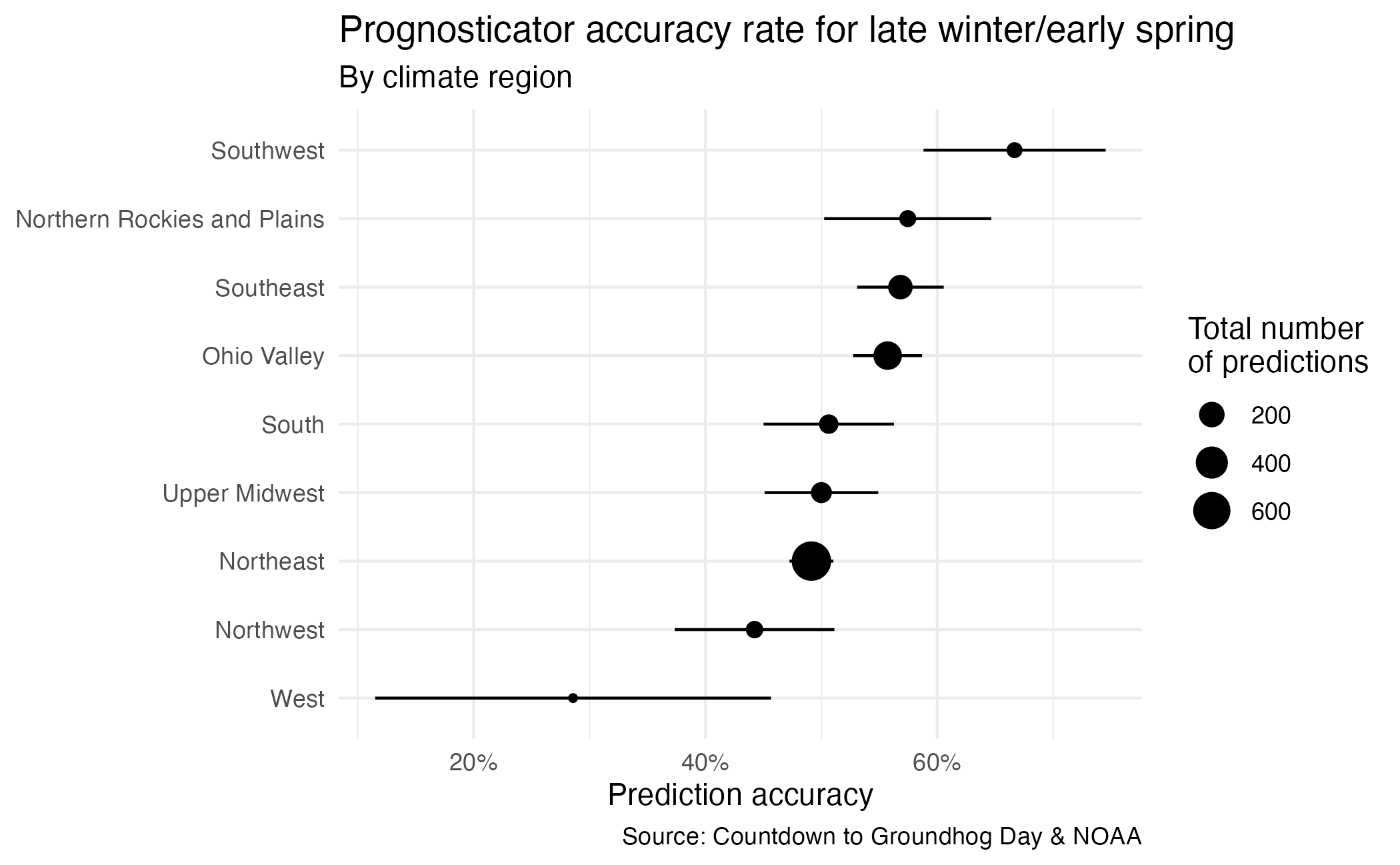
ae-03
Note
- Go to the course GitHub org and find your
ae-03(repo name will be suffixed with your GitHub name). - Clone the repo in Positron, run
renv::restore()to install the required packages, open the Quarto document in the repo, and follow along and complete the exercises. - Render, commit, and push your edits by the AE deadline – end of the day
Wrap up
Recap
- Use the
*_join()function appropriate for your analysis - Leverage the difference between mutating and filtering joins