Iteration
Lecture 13
Dr. Benjamin Soltoff
Cornell University
INFO 5001 - Fall 2023
2023-10-11
Announcements
Announcements
- Extra credit assignment
- Project proposals
Atomic vectors
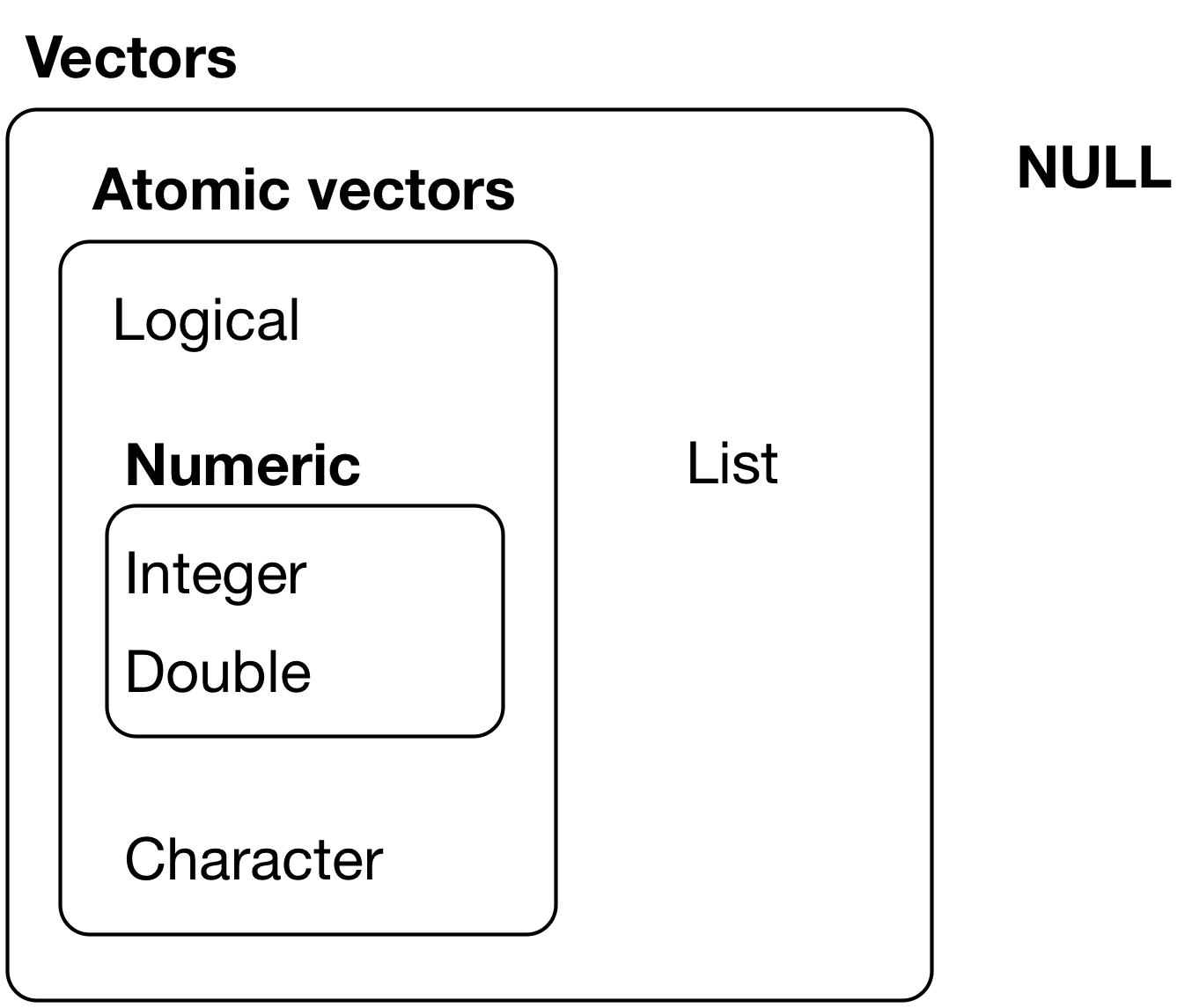
Subsetting vectors with [] and [[]]
- With positive integers
- With negative integers
- Don’t mix positive and negative
Subset with a logical vector
Lists
Lists
Lists: str()
Store a mix of objects

Nested lists
Secret lists
tibble [125 × 14] (S3: tbl_df/tbl/data.frame)
$ case : chr [1:125] "Oxford High School shooting" "San Jose VTA shooting" "FedEx warehouse shooting" "Orange office complex shooting" ...
$ year : num [1:125] 2021 2021 2021 2021 2021 ...
$ month : chr [1:125] "Nov" "May" "Apr" "Mar" ...
$ day : int [1:125] 30 26 15 31 22 16 16 26 10 6 ...
$ location : chr [1:125] "Oxford, Michigan" "San Jose, California" "Indianapolis, Indiana" "Orange, California" ...
$ summary : chr [1:125] "Ethan Crumbley, a 15-year-old student at Oxford High School, opened fire with a Sig Sauer 9mm pistol purchased "| __truncated__ "Samuel Cassidy, 57, a Valley Transportation Authorty employee, opened fire at a union meeting at the light rail"| __truncated__ "Brandon Scott Hole, 19, opened fire around 11 p.m. in the parking lot and inside the warehouse, and then shot h"| __truncated__ "Aminadab Gaxiola Gonzalez, 44, allegedly opened fire inside a small business at an office complex, killing at l"| __truncated__ ...
$ fatalities : num [1:125] 4 9 8 4 10 8 4 5 4 3 ...
$ injured : num [1:125] 7 0 7 1 0 1 0 0 3 8 ...
$ total_victims : num [1:125] 11 9 15 5 10 9 4 5 7 11 ...
$ location_type : chr [1:125] "School" "Workplace" "Workplace" "Workplace" ...
$ male : logi [1:125] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE ...
$ age_of_shooter : num [1:125] 15 57 19 NA 21 21 31 51 NA NA ...
$ race : chr [1:125] NA NA "White" NA ...
$ prior_mental_illness: chr [1:125] NA "Yes" "Yes" NA ...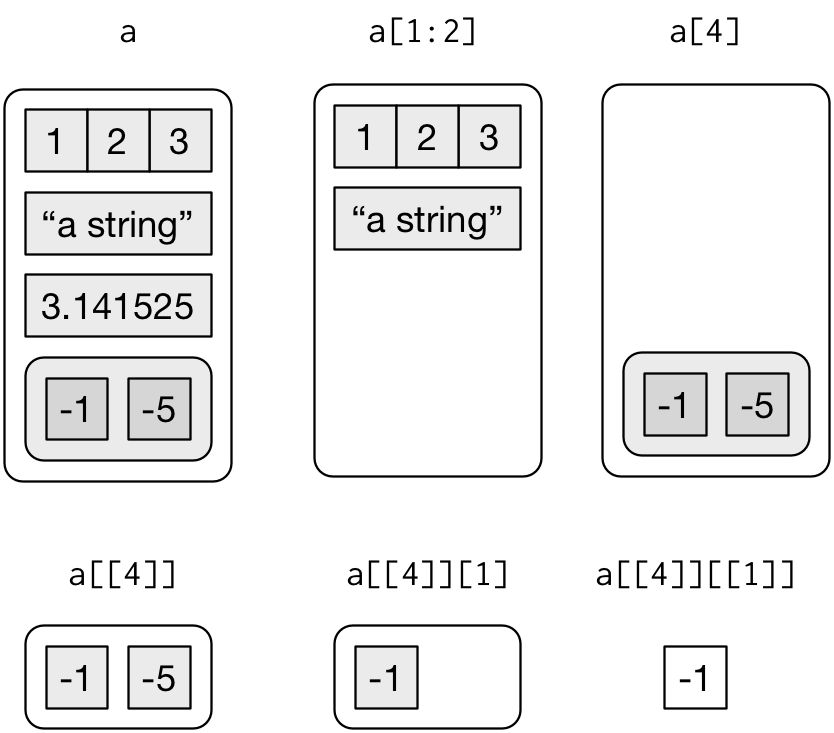
Iteration
Iteration
Iteration three ways
forloopsmap_*()functionsacross()
Iteration with for loops
Iteration with for loop
Output
Sequence
Body
Preallocation
Warning in microbenchmark(`No preallocation` = {: less accurate nanosecond
times to avoid potential integer overflows
Iteration with map_*() functions
Map functions
- Why
forloops are good - Why
map()functions may be better - Types of
map()functionsmap()makes a listmap_lgl()makes a logical vectormap_int()makes an integer vectormap_dbl()makes a double vectormap_chr()makes a character vector
Map functions
Map functions
a b c d
0.07462564 0.20862196 -0.42455887 0.32204455 Application exercise
ae-11
- Go to the course GitHub org and find your
ae-11(repo name will be suffixed with your GitHub name). - Clone the repo in RStudio Workbench, open the R script in the repo, and follow along and complete the exercises.
- Render, commit, and push your edits by the AE deadline – end of tomorrow
Recap
- Use
[],[[]], and$notation to extract elements from an atomic vector or list object forloops +map()functions are common methods for iteration in R- When using
forloops, always preallocate the output vector map()functions are a family of functions that apply a function to each element of a vector or list
Will you get lucky?
